The main page for ServiceNow training and certification can be found here: https://www.servicenow.com/services/training-and-certification.html
Leverage the ServiceNow community for help with best practices and help from the developer and administrator ecosystem: https://www.servicenow.com/community/
The best way to learn ServiceNow is by jumping into a development instance and taking the new to ServiceNow courses. https://developer.servicenow.com/dev.do
You can also go into the ServiceNow Community page and search “passing the ServiceNow CSA
https://www.servicenow.com/community/

Mark Miller’s The Complete ServiceNow System Administrator Course is for an older version with the new UI changes and current release, but is still relevant for learning the basics of administration. https://www.udemy.com/course/the-complete-servicenow-system-administrator-course/#instructor-1
The prerequisites for System Administrator Certification are:
1) Attending a ServiceNow Fundamentals live class or
2) complete the ServiceNow Fundamentals On Demand learning path.
Passing ServiceNow’s System Administrator Certification (CSA) exam demonstrates mastery of ServiceNow System Administration and shows that a candidate has the skills and essential knowledge necessary to manage the configuration, implementation, and maintenance of the ServiceNow platform. Successfully passing this certification exam also establishes the core skill set necessary to pursue further certification for individuals.
Prerequisites for System Administrator Certification are:
1) Attending a ServiceNow Fundamentals live class or complete the ServiceNow Fundamentals On Demand learning path.
2) Have at least six months of hands on experience with ServiceNow.
3) Have industry experience with database concepts and system management.
Take a look at the Next Experience Navigation documentation page to learn the basics of ServiceNow navigation and UI here: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/get-started/servicenow-overview/concept/using-the-next-experience-global-header.html
System Administrator certification is one of four mainline certifications. The four Mainline Certification job role paths are:
- System Administrator
- Implementation Specialist
- Application Developer
- Application Specialist
The ServiceNow Credentialing Program Guide can be accessed here:
https://www.servicenow.com/services/training-and-certification/journey/#/
See the CSA Exam Specification (Blueprint) here: https://www.servicenow.com/content/dam/servicenow/other-documents/training/servicenow-sys-admin-exam-specs.pdf
As you are studying and preparing for the exam, it’s best to complete all labs in the Developer Instance, including the Capstone Project. Each section has a lab verification area for confirmation you are completing everything correctly. If you can get through these labs on your own, you should be well prepared for the exam.
Here are sample definitions, questions, and answers by category that you may see on the exam, listed alphabetically. For any of these terms, it is useful to search the term in the ServiceNow documentation: https://docs.servicenow.com/
For any of these glossary terms, you can ask ChatGPT to write sample multiple choice questions. Here’s the prompt:
“I’m studying for the ServiceNow CSA exam. Please write 6 multiple choice questions I’m likely to see on the topic of [Access Control] with the correct answer letter at the bottom of each question.”
A
Access Control
Question: What define permissions in the system?
Answer: Access control rules.
Question: What are access controls assigned to?
Answer: Access control rules are assigned to roles, roles are assigned to groups, and users are assigned to groups.
Question: In which table will you find access control rules?
Answer: sys_security_acl
Question: What do all access control list rules specify?
Answer: The object and operation being secured, and the permissions required to access the object. The object is the target to which access needs to be controlled. Each object consists of a type and name that uniquely identifies a particular table, field, or record.
Question: Table access control rules are processed in which order?
Answer: Table Name > Parent Table Name > Any Table Name (wildcard *)
Question: In what order are access controls evaluated?
Answer: Access controls are evaluated first at the table-level (most specific to most general), then at the field-level (most specific to most general).
Question: Which are valid user authentication methods?
Answer: LDAP, SSO, and Local Database
Question: What must you specify when creating an access control rule?
Answer: You must specify the object (like a record) and the operation (create, read, update, delete). You must also specify the required permissions (role or set of roles, and any additional conditions).
Question: What is true in regards to access control rule evaluation?
Answer: If a row level rule and a field level rule exist, both rules must be true before an operation is allowed.
Question: To whom is an ACL defined and applied to?
Answer: A specific role or user.
Question: If a user requests access to data in a certain table, and they pass the table ACL rule but fail the field rule, what happens?
Answer: They will be granted access to the table, but not the field.
Question: Where do you see what roles and permissions a specific user has?
Answer: In the User record, you will see a list of roles that are assigned to the user. To see a User record, in the main ServiceNow browser tab, use the All menu to open User Administration > Users.
User Administration > User See List of Roles
Click a user in the User record list to view the user configuration. In the Roles related list (tab), you’ll see the roles that the user is assigned to.
Question: How can you see a list of all users with the ITIL role?
Answer: Go to the sys_user_has_role table (All > sys_user_has_role.list) search for ITIL
Question: True or false? Users can’t read, write, create, or delete data unless access controls explicitly allow those actions.
Answer: True.
Question: In order for a user to access an object, An ACL rule only grants a user access to an object, the user must meet all of the permissions required by the matching ACL rule. What must evaluate to true during the ACL evaluation process?
Answer:
• The condition must evaluate to true
• The script must evaluate to true or return an answer variable with the value of true
• The user must have one of the roles in the required roles list. If the list is empty, this condition evaluates to true
• [Record ACL rules only] The matching table-level and field-level ACL rules must both evaluate to true
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/vancouver-platform-security/page/administer/contextual-security/concept/access-control-rules.html
Question: What is the definition of Group in relation to access control?
Answer: A Group is a set of users who share a common purpose. Members of groups perform similar tasks or need access to similar information for various purposes, such as approving change requests, resolving incidents, receiving email notifications, or administering the Service Catalog. Users working in ServiceNow are typically assigned to one or more groups.
Question: How can you see a list of all groups?
Answer: All > sys_user_group.list
Question: Can a user belong to more than one group?
Answer: Yes.
Question: True or False? In the Global Domain, all users are allowed to see and manage records with permission.
Answer: True
Question: Which elevated role is required to modify access control rules?
Answer: security_admin
Question: What types of permissions can be configured in an access control rule?
Answer:
- Conditions
- Roles
- A Script that sets the answer variable to either true or false.
Question: What are the steps to implement role-based access control?
Answer: Create roles and groups, add the role to the group, then assign users to the groups.
To create a role (note – you’ll need to have the admin role), navigate to All > User Administration > Roles and create a new record.
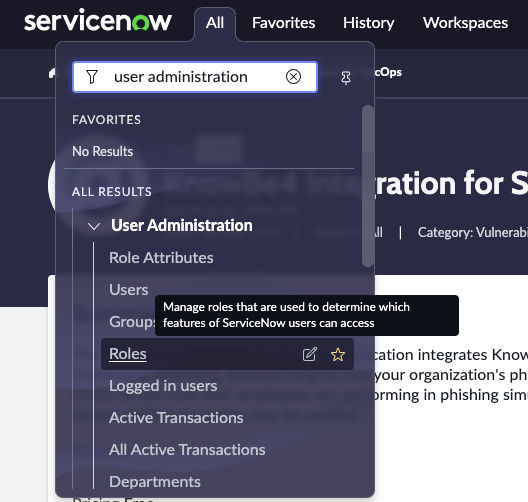
Question: How do you assign a role to a group?
Answer: Navigate to All > User Administration > Groups
- Click the group to assign a role.
- In the Roles related list, click Edit
- Use the slushbucket to add the desired roles to the group.
- Click Save
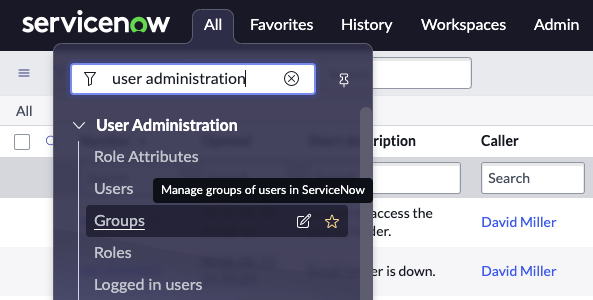
https://docs.servicenow.com/csh?topicname=t_AssignRoleToGroup.html&version=latest
Question: How do you assign a role to a user?
Answer: You will need the user_admin or admin role to be able to assign a role to a user. The steps are:
- Navigate to All > User Administration > Users and then open a user record.
- In the Roles related list, click Edit.
- In the Collection list, select the desired roles, and then click Add.
- Click Save.
https://docs.servicenow.com/csh?topicname=t_AssignARoleToAUser.html&version=latest
Question: An ACL (Access Control List) rule only grants a user access to an object if the user meets all of the permissions required by the matching ACL rule. What must occur for the user to be granted access?
Answer:
• The condition must evaluate to true
• The script must evaluate to true or return an answer variable with the value of true
• The user must have one of the roles in the required roles list. If the list is empty, this condition evaluates to true.
• [Record ACL rules only] The matching table-level and field-level ACL rules must both evaluate to true
Question: Can you restrict access to your instance by IP range?
Answer: Yes. Go to All > System Security > IP Address Access Control to see a list of your IP access controls.
https://docs.servicenow.com/csh?topicname=t_AccessControl.html&version=latest
Question: What is an example of contextual security in ServiceNow?
Answer: An ACL.
Question: What does Contextual Security Manager do?
Answer: Contextual Security Manager protects your data by controlling read, write, create, and delete authorization. The Contextual Security Manager is aware of the system table hierarchy, enabling you to create specific security rules for a field based on where in the hierarchy it is displayed. Benefits of the Contextual Security Manager include:
• Contextual Security – Secure a record based on the contents of the record.
• Hierarchical Security – Apply security rules to any level in the object hierarchy.
https://docs.servicenow.com/csh?topicname=intro-now-platform-landing.html&version=latest
Question: How do you see the out-of-the-box roles?
Answer: System Security > Users and Groups > Roles
Question: How do control access at the knowledge base level?
Answer: Through User Criteria. You specify user criteria for a knowledge base to control which users are granted access to read and contribute knowledge articles to that knowledge base.
Question: How do you create a User Criteria record in order to control access?
Answer:
Navigate to All > Knowledge > Administration > Knowledge Bases, Click the link to the knowledge base you manage, add user criteria to the knowledge base, and then depending on the user criteria you want to set, select one or more of the relevant related lists.
Question: For Knowledge, what are relevant related list options?
Answer: Can Read, Cannot Read, Can Contribute, Cannot Contribute.
https://docs.servicenow.com/csh?topicname=t_SelectUserCriteria.html&version=latest
Question: Where can you access a playbook of instance security best practices?
Answer: In the Instance Security Best Practice Playbook:
Question: What actions apply to which access operations?
Answer:
| Operation | Action |
| Execute | Run app or script |
| Create | Insert records |
| Read | Display records |
| Write | Update records |
| Delete | Remove records |
| list_edit | Update records from list view |
| report_on | Create reports |
Administration
Question: How frequently are backups of your ServiceNow data performed?
Answer: 4 weekly full backups and 6 days of daily differential backups are performed.
Question: How many past entries does the History menu show by default?
Answer: 30
Additional Actions Icon (The Hamburger Icon)
Question: Where do you find the Additional Actions Icon?
Answer: In the upper left of a Form.
YouTube tutorial: https://youtu.be/eZOTFdRmOh0?si=93FmgjycMyAfg2tM
All Menus
Question: What does the All menu allow you to do?
Answer: It lists all the menu items and modules in the instance, and allows you to retrieve the menu items and modules you have access to in your instance, favorite them, and return to items you previously visited.
Question: When you type Incident > Create New in the All menu, which is the application, and which is the Module?
Answer: Incident is the application and Create New is the Module.
Annotations
Question: What are Annotations?
Answer: Some forms have annotations. Annotations are additional information on a form intended to provide on-screen instruction to users. Annotations have dark text on a colored background. Individual users can toggle annotations on and off.
Question: How do you create an Annotation for a Form?
Answer: Navigate to All > System UI > Messages.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/form-administration/concept/c_FormAnnotation.html
App Engine Studio
Question: What is App Engine Studio?
Answer: A low-code studio with guidance and templates, visual workflow, and configurable templates.
Approval Rules
Question: How do you navigate to Approval Rules?
Answer: All > System Policy > Rules > Approval
Approvals
Question: What is an Approval?
Answer: Approvals require authorization on tasks before the work is done. You can define approvals for all tasks and associate users or groups to a task to approve or reject them.
Question: How do you navigate to Approval Rules?
Answer: All > System Policy > Rules > Approval
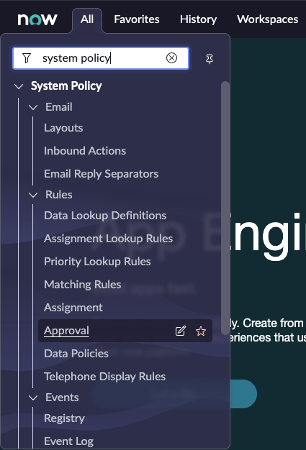
Approval Rules
Question: Can you conduct an approval with a Process Guide?
Answer: Yes.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/service-administration/task/t_ProcessGuideApprovals.html
Question: Can you assign approvals to both users and groups?
Answer: Yes.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/service-administration/reference/r_Approvals.html
Question: What is true about fulfillers and approvers?
Answer:
1) Fulfillers have the itil role and the approver_user role.
2) Approver users only have the approver_user role, and not the itil role.
Assignment Rules
Question: What are Assignment Rules?
Answer: The Assignment rules module allows you to automatically set a value in the assigned_to and assignment_group fields when a set of conditions occurs.
Question: How do you view Assignment Rules?
Answer: All > System Policy > Rules > Assignment
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/task-table/task/t_AssignmentModuleRule.html
Question: How do you create an Assignment Rule?
Answer: Navigate to All > System Policy > Rules > Assignment and click New. Complete the form.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/task-table/task/t_AssignmentModuleRule.html
Authentication
Question: What are the methods used for authentication?
Answer: Single sign-on (SSO), LDAP, and local database
Question: How do you implement Single sign-on (SSO)?
Answer: Through the plugin. Go to System Definition > Plugins > *single > click the plugin named Integration Multiple Provider Single Sign-On Installer. Click activate to activate the plugin.
Question: What does LDAP stand for?
Answer: Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
Automated Test Framework
Question: What is the Automated Test Framework?
Answer: The Automated Test Framework (ATF) enables you to create and run automated tests to confirm that your instance works after making a change. For example, after an upgrade, during application development, or when deploying instance configurations with update sets. Review failed test results to identify the changes that caused the failure and the changes that you should review.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/auto-test-framework/concept/automated-test-framework.html
B
Base System
Question: What are examples of Base Systems?
Answer: Incident, Problem, Change Request, and Knowledge.
Basic Configuration
Question: What can you configure with Basic Configuration?
Answer:
1) Page top banner – text / logo / color
2) Timezone, date, and time formats
3) Page header caption
4) Banner and list caption background color
5) Browser tab title
6) Banner image
7) System timezone for all users unless overridden in the user’s record
Question: How do you access Basic Configuration?
Answer: System Properties > Basic Configuration.
Business Rule
Question: What is a Business Rule?
Answer: A server-side script configured to run when a record is displayed, updated, deleted, or when a table is queried. You use business rules to accomplish tasks like automatically changing values in form fields when certain conditions are met, or to create events for email notifications and script actions.
Question: Can a Business Rule be a piece of Javascript?
Answer: Yes.
Question: When do Business Rules run?
Answer: When a record is displayed, inserted, updated, or deleted, or when a table is queried.
Question: What two sets of criteria determine when Business Rules run?
Answer:
- The time that the business rule is configured to run relative to a record being modified or accessed.
- The database operation that the system takes on the record.
Question: What determines the time that Business Rules run?
Answer:
| Option | When the rule runs |
|---|---|
| Before | After the user submits the form but before any action is taken on the record in the database. |
| After | After the user submits the form and after any action is taken on the record in the database. |
| Async | When the scheduler runs the scheduled job created from the business rule. The system creates a scheduled job from the business rule after the user submits the form and after any action is taken on the record in the database. Note: Newly created business rules will run during upgrades. |
| Display | Before the form is presented to the user, just after the data is read from the database. |
Question: When are some common tasks accomplished by Business Rules?
Answer:
- Automatically change values in form fields when certain conditions are met.
- Create events for email notifications and script actions.
- Create an associated CI when a new asset is created.
- Increment the reopen count when an incident is reopened.
Question: Do Business Rules contain Javascript?
Answer: Yes.
Question: Is a Business Rules a customization?
Answer: Yes.
Question: In which table are Business Rules stored?
Answer: sys_script
Question: How is order determined for a Business Rule?
Answer: When you enter a number that indicates the sequence in which this business rule should run. If there are multiple rules on a particular activity, the rules run in the order specified here, from lowest to highest.
C
Catalog Builder
Question: What can you do in Catalog Builder?
Answer:You can create or edit a catalog item (catalog item or record producer) using a visual and guided experience along with specified restrictions. The catalog builder experience enables you to delegate the creation and maintenance of the catalog.
You can also create a template that can be used to create catalog items. While creating the template, you can specify values or restrictions for items created using the template, for example, restrictions to catalogs, categories, variable types, and portal settings.
From the home page of the catalog builder, you can do the following:
• Create a catalog item
• Create a catalog item template
• View the available catalog items
• View the available catalog item templates
• View catalog items that are recently updated
• View the configured content that describes the catalog building process in your organization.
Question: A catalog item goes through various states during the item creation and maintenance process. What are those states?
Answer: Draft, Publishing, and Published.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/catalog-builder.html
Change Management
Question: What does a Change Request enable?
Answer: A change request enables you to implement a controlled process for the addition, modification, or removal of approved and supported configuration items (CIs). A change request records the detailed information about the change, such as the reason of the change, the priority, the risk, the type of change, and the change category.
Question: What are the three options for creating a Change Request?
Answer: 1) From the Change module 2) From an incident or a problem 2) From an existing change record
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/change-management/task/t_CreateAChange.html
Question: What are the three types of Change Requests?
Answer: Normal, Standard, or Emergency changes.
Question: What are eight Change States that may be applied depending on the type of Change Request (Normal, Standard, or Emergency changes)
Answer:
- New
- Assess
- Authorize
- Scheduled
- Implement
- Review
- Closed
- Canceled
Question: What are Standard Changes?
Answer: Standard changes are pre-approved, low risk changes with a proven history of success. The standard change catalog contains the changes that have been approved by the Change Management application as standard changes. Users with the ITIL role can view the list of available standard changes and submit change requests.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/change-management/concept/c_StandardChangeCatalogPlugin.html
CI Configuration Item
Question: A CI is what?
Answer:
- Intangible (business services, email, etc.)
- Tangible (hardware, software, servers, etc.)
- A Configuration Item
Question: Can a CI be a user or a group?
Answer: No
Client Scripts
Question: What are Client Scripts used for?
Answer: For making changes to the appearance of forms, displaying different fields based on values that are entered, or other custom display options.
Question: What are four types of Client Scripts supported in ServiceNow?
Answer: onCellEdit, onLoad, onSubmit, and onChange.
Question: What is true of Client Scripts and Business Rules?
Answer: A Client Script runs on the client when onLoad or onChange of a field occurs, or when onSubmit of a record occurs. A Business Rule runs on the server before or after a record is loaded, inserted, deleted or updated.
Question: What does the g_scratchpad object do?
Answer: The g_scratchpad object passes information from the server to the client, such as when the client requires information not available on the form. For example, if you have a Client Script which needs to access the field u_retrieve, and the field is not on the form, the data is not available to the Client Script. A typical solution to this situation is to place the field on the form and then always hide it with a Client Script or UI Policy. While this solution may be faster to configure, it is slower to execute.
https://developer.servicenow.com/dev.do#!/guides/sandiego/now-platform/tpb-guide/client_scripting_technical_best_practices%23%23example-g-scratchpad#example-g-scratchpad-
Question: How do you access Client Scripts?
Answer: Through the All Menu > System Definitions > Client Scripts
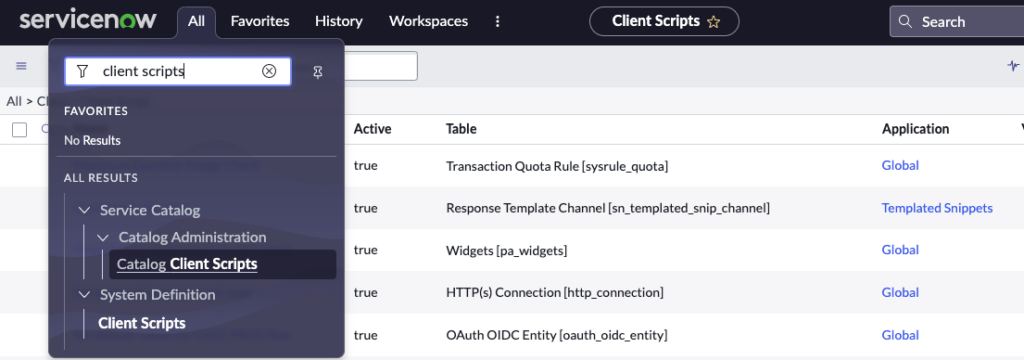
CMDB Configuration Management Database
Question: What are the three main tables in the CMDB?
Answer:
- Configuration Item [cmdb_ci]
- Base Configuration Item [cmdb]
- CI Relationship [cmdb_rel_ci]
Question: Which table stores information about CI relationships?
Answer: cmdb_rel_ci
Question: What is used to create dependencies between configuration items in the CMDB?
Answer: You use the CI Class Manager to centrally view, create, or edit basic class definitions, and class settings for identification, reconciliation, and CMDB Health. To access the CI Class Manager, navigate to All > Configuration > CI Class Manager.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/configuration-management/reference/ci-class-manager-landing-page.html
Question: What does a CI (Configuration Item) record contain?
Answer: A CI record contains all of the relevant attribute data about an item such as name, version, descriptions, ownership, etc., which are documented in fields on the form.
Question: When you extend a table in the CMDB, does the table also inherit relationships from the table it is extending?
Answer: Yes, and you can create a new relationship rule in Configuration > Relationships > Suggested Relationships.
Question: What are Quick start tests for Configuration Management Database (CMDB)?
Answer: Quick start tests for CMDB allow you to validate that your Configuration Management Database (CMDB) still works after you make any configuration change such as apply an upgrade or develop an application. You copy and customize these quick start tests to pass when using your instance-specific data.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/atf-quick-start-tests/reference/quick-start-tests-cmdb.html
Question: What are four main concepts associated with CMDB?
Answer: Dependency Views, A Database, Service Processes, Tables and Fields
Question: What are Dependency Views?
Answer: Dependency Views graphically displays an infrastructure view for a configuration item (CI) and the application or business services that it is part of and that it supports. Dependency Views indicates the status of its configuration items, and allows access to CIs related alerts, incidents, problems, changes, and services. If Service Mapping is activated, Dependency Views maps are enhanced to display dependencies that reflect connections in service maps.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/business-service-management-map-ng/concept/c_BusinesssServiceManagementMaps.html
Question: What are options for populating the CMDB?
Answer: Either by using Discovery, by using the IntegrationHub ETL or Import Sets to import and integrate data from a third-party source, by integrating with an external CMDB, or by manually creating CIs.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/configuration-management/concept/c_OptionsToPopulateCMDB.html
Question: What are four concepts related to CMDB?
Answer:
1) Service Processes
2) Tables and Fields
3) A Database
4) Dependency Views
Coalesce
Question: When fields are coalesced during an import, what happens?
Answer: If a match is found using the coalesce fields, the existing record is updated with the information being imported.
Question: What does the Coalesce option allow you to update when transforming import data?
Answer: The Coalesce option allows you to update existing target table records when transforming import data.
Question: How do you avoid creating duplicates while importing data?
Answer: Use the Coalesce field.
Question: When importing data, what happens when you specify a field as Coalesce?
Answer: Making sure the field will be used as a unique key during import.
Question: What are several possible configurations you can use to coalesce data in import sets?
Answer:
• No Coalesce
• Single-field Coalesce
• Multiple-field Coalesce
• Conditional Coalesce
Conditions and Condition Builder
Question: What does the Condition Builder do? Can you save and copy conditions?
Answer: A Condition Builder constructs a condition statement with a series of contextually generated fields. Condition builders are used in many operations, such as creating filters, administering surveys, and administering access control. Yes, you can copy and save conditions.
Question: A condition consists of three parts. What are they?
Answer: Field, Operator, and Value.
Question: A condition consists of three parts. What are they?
Answer: Field, Operator, Value, and Grouping.
• Field: Each field contains data from a particular column in the table. Selecting a reference field enables you to dot-walk to data from other tables.
• Operator: Each field type has its own set of valid operators. The operator determines if a value is needed.
• Value: Each field has its own set of valid values determined by the field type. Reference fields have access to auto-complete, and choice lists provide a list of options.
• Grouping: Each condition line is grouped with either an AND or an OR connector. The filter requires all condition lines linked with an AND connector to be met. The filter separately evaluates each condition line linked with an OR connector.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/concept/c_Filters.html
Question: How do you open the Condition Builder?
Answer: By clicking the Filter icon (the funnel icon) in the list header.
Question: How do you remove a condition?
Answer: Remove the condition from the breadcrumbs by clicking the Remove next condition (>) icon for the condition.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/common-ui-elements/concept/c_ConditionBuilder.html
Configuration Item (CI)
Question: What is a configuration item?
Answer: ITIL 4 defines a CI as any component that needs to be managed in order to deliver an IT service.
Question: Can configuration items be tangible AND intangible?
Answer: Yes
Question: What are some examples of configuration items?
Answer: Servers, laptops, desktops, software applications, routers, and switches.
Question: What is a CI class?
Answer: A category – for example, servers. You can also have child classes like Windows or Linux servers. Each CI class has its’ own table, and there are hundreds of them.
Question: CIs are records in which table?
Answer: In the cmdb_ci table, or any of its’ extended tables.
Connect Chat
Question: What is Connect Chat?
Answer: Connect Chat is a real-time messaging tool that enables users to chat with individuals and groups, quickly share files, and collaborate on any record by connecting with the right people instantly.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/use/collaboration/concept/c_Collaboration.htm
*Note that as of the Vancouver Release, Connect Chat has been replaced by Sidebar. See the Sidebar documentation: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/vancouver-servicenow-platform/page/administer/conversational-interfaces/concept/sidebar-landing.html
Connect Workspace
Question: What is Connect Workspace?
Answer:
The Connect workspace is a full-screen view of all your Connect Chat and Connect Support conversations in one place. It contains the conversation pane, which displays the conversation header and an expanded version of the mini window, and the conversation tools area.
To open the Connect workspace, navigate to Collaborate > Connect Chat or click the new window icon
(![]() ) in a Connect mini window. If you do not have any recent conversations, a screen appears with helpful information about Connect.
) in a Connect mini window. If you do not have any recent conversations, a screen appears with helpful information about Connect.
Question: How do you open Connect Workspace?
Answer: Navigate to Collaborate > Connect Chat or click the new window icon () in a Connect mini window. If you do not have any recent conversations, a screen appears with helpful information about Connect.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/use/collaboration/concept/c_CollaborationWorkspace.html
Content Frame
Question: What is the main area of the web page in ServiceNow?
Answer: The Content Frame.
Context Menu (the hamburger icon)
Question: How do you access a form context menu?
Answer: By clicking the icon beside the form title (the hamburger icon), or right-clicking the form header.
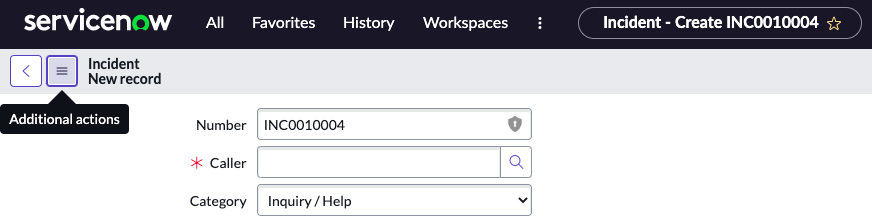
Once you click the Additional Actions / Context Menu / Hamburger icon, you will be presented with options to configure the form, export, create a favorite, and other options.
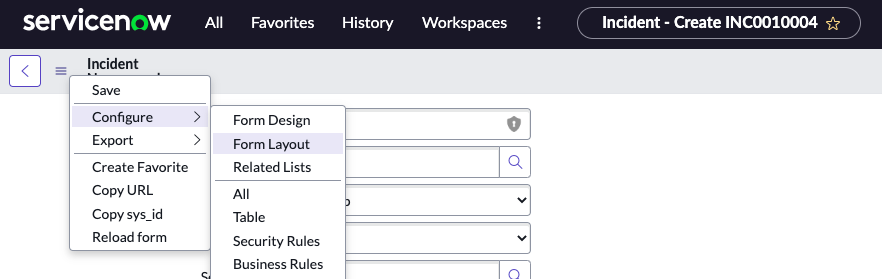
Question: Context Menus are analogous to the application menus of a program on your computer.
Answer: True.
Question: How can Administrators customize some of the options available on a Context Menu?
Answer: By using UI Actions
Question: What are some common actions you can take from the column Context Menu?
Answer: Create quick reports, configure the list, and export data.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-forms/concept/c_FormContextMenu.html
Contextual App Pill
Question: What does the Contextual App Pill allow you to do?
Answer: See where you are in the instance, and favorite the current item by clicking the star icon.
Question: What provides the context for where you are in the system?
Answer: The Contextual App Pill
Contextual Security Manager
Question: What does Contextual Security Manager do?
Answer: Contextual Security Manager protects your data by controlling read, write, create, and delete authorization. The Contextual Security Manager is aware of the system table hierarchy, enabling you to create specific security rules for a field based on where in the hierarchy it is displayed.
Benefits of the Contextual Security Manager include:
• Contextual security – Secure a record based on the contents of the record.
• Hierarchical security – Apply security rules to any level in the object hierarchy.
Question: True or False? In the Contextual Security Manager, you have the ability to set the maximum attachment size and specify the attachment file types.
Answer: True
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/roles/reference/r_ContextualSecurity.html
CSS Properties
Question: Where do you go in ServiceNow to change the banner and colors?
Answer: System Properties>CSS properties
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/administer/navigation-and-ui/reference/customizing-instance-appearance.html
Customizations
Question: Where are common places customizations are applied?
Answer:
- Client Scripts
- Business Rules
- Data Policies
- UI Actions
- UI Policies
Question: How do you revert / overwrite a customization?
Answer: To prevent customizations from being overwritten by system upgrades, the upgrade process automatically skips changes to objects that have been customized. You may want to overwrite your customizations when a software upgrade contains a feature that you would like to implement.
Procedure
- Navigate to All > Upgrade Center > Upgrade History.
- Select the desired software version.
- Filter the Upgrade Details related list by Disposition is Skipped.
- (Optional) Add another filter condition for Changed is True to return only the objects that have changed since the last upgrade.
- Select the update record to implement.The File differences field displays a side-by-side comparison of the customization and the default version. Deletions are highlighted in red, additions in green, and modifications in yellow.
- Click Revert to base system to overwrite your customized object with the system default version.
- The Disposition changes from Skipped to Reverted.
- After you revert a customization, you have the option to click Reapply Changes to reapply your customizations (undo the revert).
D
Dashboards
Question: What do Dashboards allow you to do?
Answer: Dashboards enable you to display multiple performance analytics, reporting, and other widgets on a single screen. You use dashboards to create a story with data that you can share with users.
Question: Can any user create a new dashboard?
Answer: Yes.
Question: What can you incorporate into Dashboards?
Answer: Gadgets, reports, and widgets.
Question: What are Widgets?
Answer: Widgets are objects that have been added to dashboards. You can create and manage widgets. Many applications have their own widgets. See an application’s documentation for information about the widgets included with the application.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/use/dashboards/concept/widgets.html
Data Policies
Question: What do Data Policies allow you to do?
Answer: Data policies enable you to enforce data consistency by setting mandatory and read-only states for fields. Data policies are similar to UI Policies, but UI Policies only apply to data entered on a form through the standard browser. Data policies can apply rules to all data entered into the system, including data brought in through import sets or web services and data entered through the mobile UI.
Question: Are data policies a common customization in ServiceNow?
Answer: No.
Question: Do Data Policies run client side or server side?
Answer: Server side. https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/field-administration/concept/c_DataPolicy.html
Question: How do you create a Data Policy?
Answer: Follow the procedure below, starting with System Policy > Rules > Data Policies:
- Navigate to Data Policies by completing one of the following actions:
Navigate to System Policy > Rules > Data Policies
From any form header, right-click the header bar and select Configure > Data Policies
In List v2, open any column context menu and select Configure > Data Policies
In List v3, open the list title menu and select Configure > Data Policies - Click New
- Select any options for the data policy.
- Create the condition that must exist for the platform to apply this policy. For example, your conditions might include [Problem state] [is] [Closed/Resolved]
- Right-click the header and select Save. The Data Policy Rules related list appears.
- Click New in the related list and create the record that identifies the field and the policy to apply.
- Click Submit.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/field-administration/task/t_CreateADataPolicy.html
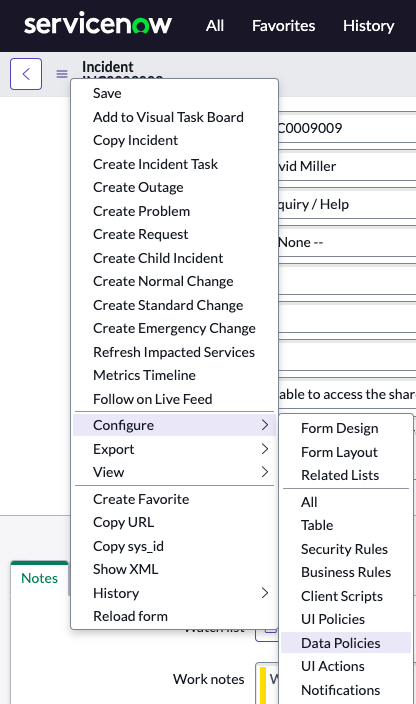
Question: What is another way to create a Data Policy?
Answer: Open an incident. Click the main Context Menu in the upper left, then Configure>Data Policies
Question: Are data policies one of the primary tools you use to automate ServiceNow?
Answer: Yes. UI policy, Data Policies, UI Actions, and scripts are all primary tools used to automate ServiceNow.
Question: How would you create a data policy for incident forms?
Answer: 1. Go to all open incidents: Incident > Open
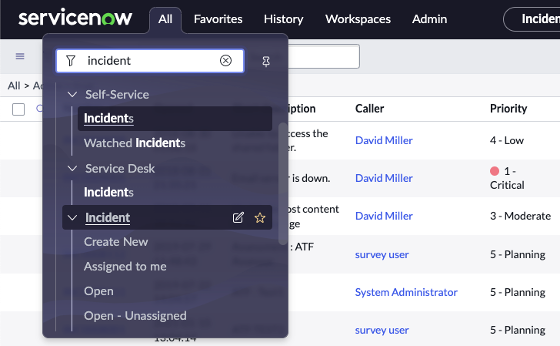
2. Right click the header bar, then Configure > Data Policy
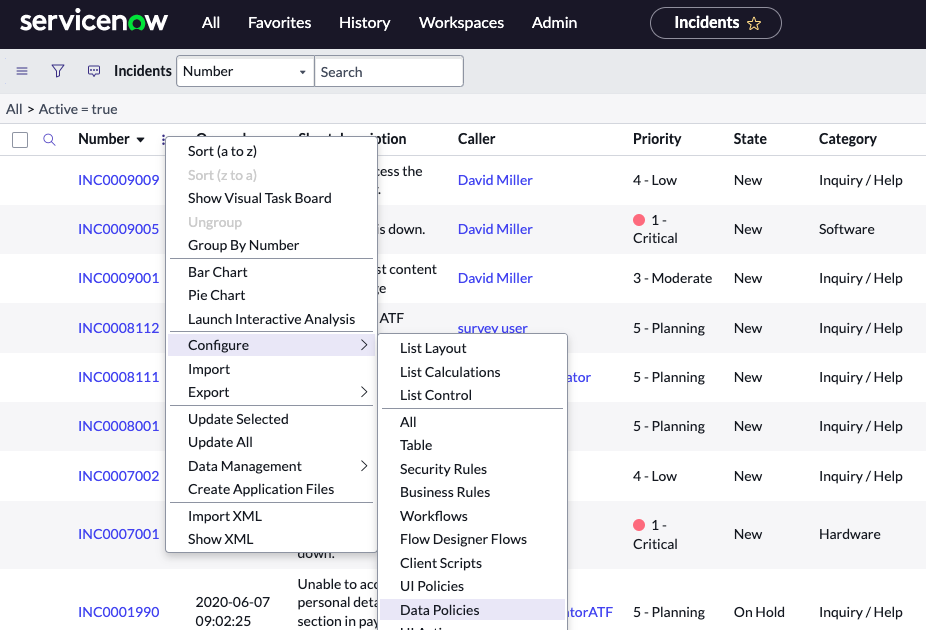
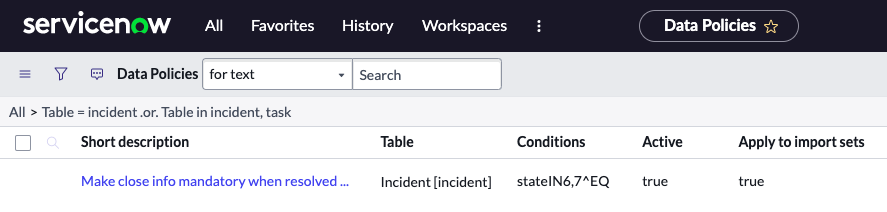
3. Note that for Incident, there is only one Data Policy written (Make close info mandatory…)
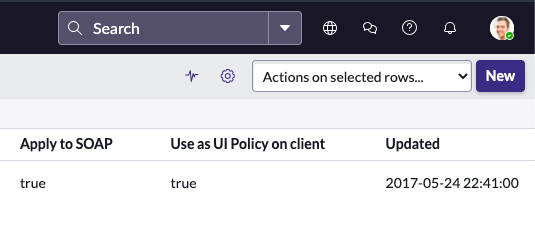
4. To create a new policy, click the New button in the upper right.
Delegate Approvals and Tasks
Question: How do you delegate approvals and tasks if you’re going to be absent from work, and need to delegate tasks and approvals?
Answer: Go to All > Self Service > My Profile. In the Delegates related list, click New.
Question: What would you call a user who is assigned to another person’s tasks and messages like approval requests?
Answer: You would call them a delegate.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/use/employee-self-service/task/t_DelegateApprovalsTasks.html
Delegated Development and Deployment
Question: What is Delegated Development?
Answer: Delegated Development helps IT extend app development to other employees while maintaining control and governance over your instances.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/applications/concept/c_DelegatedDevelopment.html
Dictionary Overrides
Question: What do Dictionary Overrides allow you to do?
Answer: Dictionary overrides provide the ability to define a field on an extended table differently from the field on the parent table.
For example, for a field on the Task [task] table, a dictionary override can change the default value on the Incident [incident] table without affecting the default value on Task [task] or on Change [change].
Administrators can override these aspects of a field:
• Reference qualifiers
• Dictionary attributes
• Default values
• Calculations
• Field dependencies
• Default column display values
• Mandatory and read-only status
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/data-dictionary-tables/concept/c_DictionaryOverrides.html
Domain Separation
Question: How do you activate domain support features?
Answer: Domain support features are activated with a plugin called Domain Support – Domain Extensions Installer. Administrators can request activation of this plugin.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/company-and-domain-separation/task/t_ActivateDomainSeparation.html
Dot-walking
Question: What is Dot-walking?
Answer: Dot-walking provides access to fields on related tables from a form, list, or script.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/navigation/concept/c_DotWalking.html
Question: What are different methods of Dot-walking?
Answer: From List Fields, Condition Builder, List Collectors, Scripts, Variables, and Tree Pickers.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/navigation/reference/dot-walking-examples.html
E
The Edge
Question: What is The Edge?
Answer: The Edge is a toolbar on the left side of the screen which provides quick access to features such as bookmarks and flyout windows. The Edge became available in UI15. The collapsed view of the UI16 application navigator is similar to the Edge.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/administer/navigation-and-ui/concept/c_TheEdge.html
Event
Question: What is an Event?
Answer: Events are special log records the system generates when something notable has happened or certain conditions are met.
Question: What are some examples of Events?
Answer:
• When a user logs in
• When someone approves a request
• When someone submits a new KB (knowledge base) article
Question: How can you view Events in the System Log?
Answer: In the Event Log
Question: What is an Event Log?
Answer: The Event Log records all system events that occur within the Now Platform.
Question: How do you navigate to Events in the System Log?
Answer: Navigate to All > System Policy > Events > Event Log
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/platform-events/event-logs-2.html
Question: How would you see login events?
Answer: Search for login events.
Event Registry
Question: What is the Event Registry?
Answer: The Event Registry lists the events the system recognizes. You use registered events to automate other activities, such as script actions or notifications.
After you create a new event and a business rule that uses the event, you must register it. Registration lets other parts of the system, such as Email and SMS notifications and Script Actions, see the event in their list of available events and react to the event when it occurs.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/platform-events/concept/c_EventRegistry.html
Question: How do you register an Event?
Answer: Navigate to System Policy > Events > Registry, and then click New.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/platform-events/task/t_RegisterAnEvent.html#t_RegisterAnEvent
Question: What is the difference between an Event Log and the Event Registry?
Answer: The Event Log records all system events that occur within the Now Platform, and the Event Registry uses registered events to automate other activities, such as script actions or notifications. The Event Log contain generated Events, and the Event Registry is a table of Event definitions.
Execution Contexts
Question: What does the Execution Contexts feature allow you to identify?
Answer: The Execution Contexts feature enables you to identify the order of execution of concurrent import sets. You can also open the import set records to access the import log.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/import-sets/task/monitor-sched-import-executions.html
Question: What are two ways of generating Events?
Answer:
• Server-side script
• Workflow Create Event activity
https://developer.servicenow.com/dev.do#!/learn/courses/sandiego/app_store_learnv2_automatingapps_sandiego_automating_application_logic/app_store_learnv2_automatingapps_sandiego_scheduled_script_executions_and_events/app_store_learnv2_automatingapps_sandiego_generating_events
Execution Plan
Question: What is an Execution Plan?
Answer: An Execution Plan describes how a catalog item is procured, configured, and installed.
Execution Plans enable you to describe simple, linear processes. Each execution plan contains one or more tasks. For example, an organization could create an execution plan for delivering a corporate standard PC that contains these tasks:
- Procure the PC from a supplier.
- Configure the PC according to requester specifications.
- Deliver the PC to the requester.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_ExecutionPlans.html
Events
Question: What are Events in ServiceNow?
Answer: Events are special records the system uses to log when certain conditions occur and to take some kind of action in response to the conditions. The system uses business rules to monitor for system conditions and to generate event records in the Event [sysevent] table, which is also known as the event log or event queue.
Question: What triggers Events?
Answer: Workflow Scripts and Business Rules.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/platform-events/concept/events.html
Extended Tables
Question: When extending a table, what is inherited?
Answer: The new table inherits the parent table’s columns as well as its business logic.
Question: What is the most commonly extended table?
Answer: The most commonly extended table is the Task table.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/app-engine-studio/task/use-existing-table.html
F
Favorites
Question: Application menus and modules that you want to access frequently and want to bookmark are referred to as what?
Answer: A Favorite.
Question: How would you go about creating a favorite for unassigned active Incidents?
Answer: Click the List Controls icon (the hamburger icon), and drop down Filters > Active – Unassigned. Go to List Controls again, and Click Favorite.
Fields
Question: What are Fields in ServiceNow?
Answer: Fields store the actual data.
Question: Why are Reference Fields important?
Answer: They reference other fields in the database.
Question: What are examples of field types in ServiceNow?
Answer: There are a variety of different field types, such as: Choice, Date/Time, Journal, Reference, and more. Field types define how a field is interacted with through the interface, as well as the type and format of data it can store.
Question: What are the two ways users enter data into a Field?
Answer: By using the list editor or by using a form. In form view, fields appear as fields in the form, and in list view they appear as columns of data in the table.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/task/t_UseTheListEditor.html
Question: Fill in the blank. Each _ corresponds to a field on the table.
Answer: Column
Question: Which one of the following modules can be used to view field settings for a table?
Answer: Tables & Columns.
Question: What types of fields are supported in ServiceNow?
Answer: HTML, String, and Script
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/time/reference/r_UseDateAndTimeFields.html
Field Types
Question: What Field Types are available?
Answer: Choice Lists, Date / Time, Image, and many more.
For the full list, go to the documentation: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/reference-pages/reference/r_FieldTypes.html
Question: What is a Choice List?
Answer: A Choice List is a type of field that lets the user select from a pre-defined set of choices.
Administrators can define the available choices and customize the behavior and appearance of choice lists.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/field-administration/concept/c_ChoiceLists.html
Filter Navigator
Question: How do you access the Filter Navigator?
Answer: From the All Menu
Question: How do you display the list view of a table in the Filter Navigator in the content frame?
Answer: Type a table name in the Filter Navigator, and append it with .LIST. After searching sys_user.LIST for example, you’ll see a list of users in the Content Frame. If you want to search for a form, append the table with .FORM. For example sys_user.FORM
Filters and Search
Question: What does the show / hide filter icon look like?
Answer: Like a funnel.
Question: What do Filters help you do?
Answer: Filters determine which table records are displayed in a list. When a developer creates a list module, the filter conditions are set. You apply filters to narrow results down to exactly what you need.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/concept/c_Filters.html
Question: In what order should filter elements be specified?
Answer: Field, Operator, then Value. i.e. Priority (Field) is (Operator) Critical (Value).
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists-v3/task/t_CreatingFiltersListV3.html
Click Show/Hide Filter
Type priority
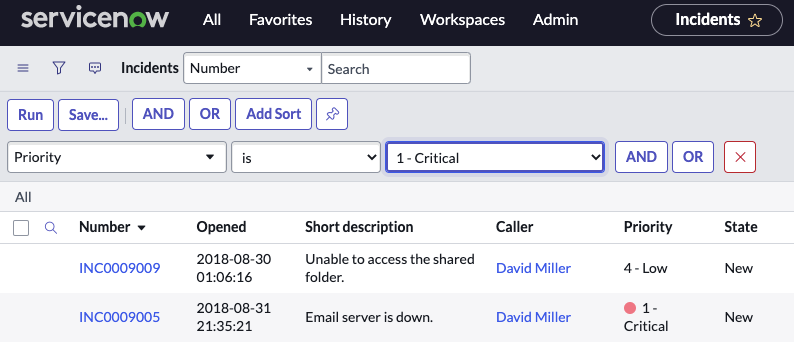
Priority is Critical
Question: What does the Global Search Filter do?
Answer: Helps you search across your instance for any related items.
Question: How do you access the Global Search Filter?
Answer: In the upper right corner.
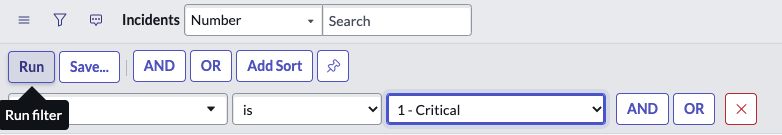
Question: How do you apply a Filter to a List?
Answer:
1) Click the Filter icon in the list header.
2) Set the [Field], [Comparison operator], and [Value] values. i.e. Priority is Critical.
3) Use the AND button or the OR button to add additional conditions to the filter as required.
4) Click the Run button to apply the filter to the list. Only records meeting the filter condition appear in the list and the breadcrumbs are updated.
Note the breadcrumbs All > Priority = 1 – Critical
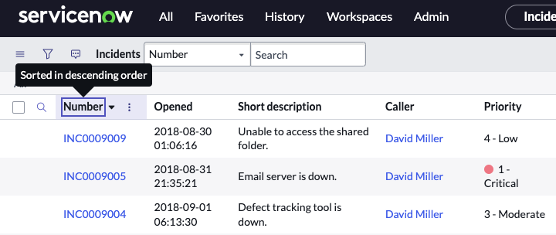
Question: What is the Sort Indicator?
Answer: The caret that tells you whether you are sorting the List in ascending or descending order.
Question: True or false? You can filter on any field, not just those displayed in the list.
Answer: True.
Question: What hides or displays the column search fields?
Answer: The magnifying glass shows the column search.
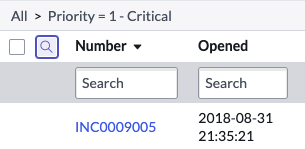
Question: What are the steps to sharing visibility of a filter with either just yourself (me), Everyone, or a specific Group?
Answer: Procedure
- Create or modify a filter in the filter interface.
- Click Save… (or Save Filter in List v3).
- Enter a name for the filter.
- Select one of the following visibility options:
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/task/t_SavingFilters.html
Flows and Flow Designer
Question: What is Flow Designer?
Answer: Flow Designer is a non-technical interface for building and enabling process automation capabilities (Flows).
Question: Which of the following are Flow Designer Triggers?
Answer: Record-based, schedule-based, or application-based.
Question: Does Flow Designer require scripting experience?
Answer: No
Question: What initiates a Flow?
Answer: A Trigger.
Question: When does a Trigger start a Flow?
Answer: A Trigger starts a flow when the conditions of the trigger are met. Triggers can be record-based, schedule-based, or application-based.
Question: How do you assign a Trigger to a Flow?
Answer: Create the Trigger first, then use Flow Designer to specify the Flow that the Trigger executes. The flows provide alerts for unexpected behavior. Navigate to All > MetricBase > Flow Designer then follow these instructions: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/metricbase/task/assign-trigger-to-workflow.html
Question: What are actions in Flow Designer?
Answer: Actions are operations executed by Flow Designer, such as looking up a record, updating a field value, requesting an approval, or logging a value.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/product/rpa-studio/concept/flow-designer-components.html
Question: What does Process Automation Designer allow you to do?
Answer: Process Automation Designer enables process owners to author cross-enterprise workflows and create a single, unified process. You can also use Process Automation Designer to provide end users with a simplified, task-oriented view of your process. You can organize Flow Designer content into unified and digitized cross-enterprise processes.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/process-automation-designer/concept/process-automation-designer.html
Question: When designing a flow, you create an action on the incident record and you need to make use of the record you created in a subsequent action. What would be useful in this situation?
Answer: A Data Pill.
Question: What are Data Pills?
Answer: Each time you add an action to a flow, Flow Designer adds a Data Pill to store its results. The data pill name indicates its sequence in the flow and its data type. Flow designers use action result data pills to provide input for other flows, actions, or subflows. Flow designers can use the sequence value in the data pill name to ensure that they select the correct data pill as an input value. When a flow runs an action, it generates the data pill runtime value, which remains the same for the duration of the flow. For example, if a data pill for [Trigger->Incident record] gets populated with incident record values at the start of a flow, the data pill preserves these values for the rest of the flow.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/flow-designer/concept/data-population.html
Formatter
Question: What is a Formatter?
Answer: A formatter is a form element used to display information that is not a field in the record. Add formatters to a form by configuring the form.
Question: How many columns can a formatter contain in a variable set?
Answer: 2
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/form-administration/concept/c_Formatters.html
Forms
Question: What is a Form?
Answer: A Form is a content page displaying fields and values for a single record from a database table. Forms have a 1-column layout, a 2-column layout, or a mix of both. Forms are opened from modules in the All menu or by clicking a record’s number in a list.
Question: What term is used to describe all the data saved within a particular form?
Answer: A Record.
Question: What do forms display?
Answer: Forms display information from one record in a table.
Question: What are the layout options with Forms?
Answer: Forms have a 1-column layout, a 2-column layout, or a mix of both.
Question: What is used to group related fields on a form together?
Answer: Sections.
Question: How do you add a Form Section?
Answer:
- Right-click the form header and select Configure > Form Layout
- In the Form view and section area below the slushbucket, click New in the Section list.
- In the Section caption field, give the new section a title, then click OK.
The rest of the instructions on adding a Section can be found here: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/form-administration/concept/configure-form-layout.html
Question: How do you open Forms?
Answer: Forms are opened from modules in the All menu or by clicking a record’s number in a list.
Opening a Form From the All Menu:
Opening an Incident Form Form From List View. Select INC0009005.
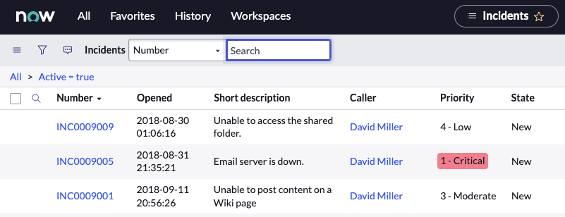
Sample incident form:
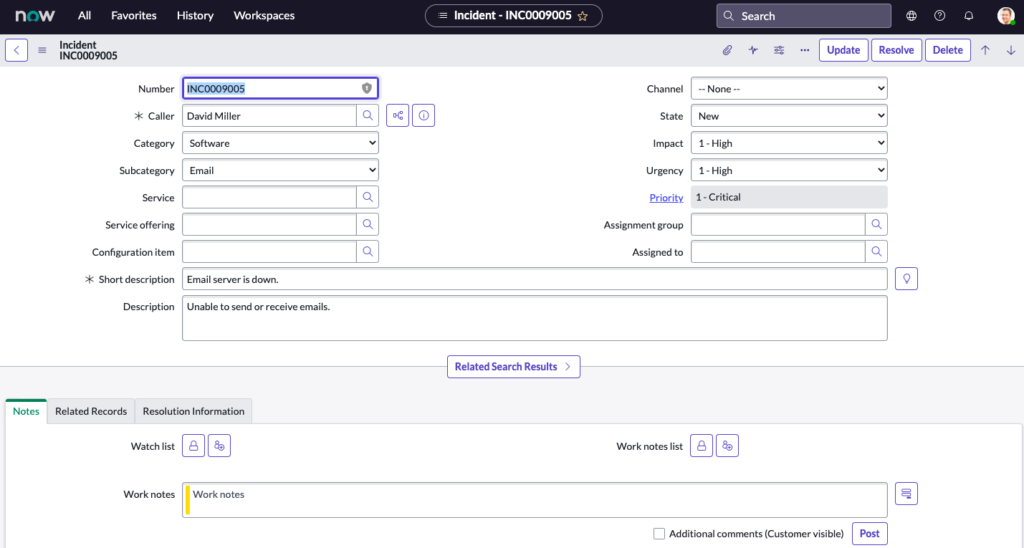
Question: What is another method of opening a new Form?
Answer: You can also append the table name with .FORM to open a new form. Examples would be sys_user.FORM or incident.FORM
Here we type incident.form in the All menu to open a new incident form.

Question: What are forms used for?
Answer: To create, view, or modify a specific record in a data table.
Question: Where are forms displayed?
Answer: In the Content Frame.
Question: What can users do in Forms?
Answer: View and edit records in Forms.
Question: What is the difference between Save and Insert actions on a Form?
Answer: Save will save the record and stay on the same form. Insert creates a new record and redirects you to list view.
Question: What is the difference between Insert and Update actions on a Form?
Answer: Insert saves changes and remains on the Form. Update saves changes and exits the Form.
Question: Where do you access form templates?
Answer: Through the More Options (the three dots) on the Form Header.
Question: How is the form context menu accessed?
Answer: You access the form context menu by clicking an icon beside the form title or by right-clicking the form header.
Question: What are sections in Forms?
Answer: Sections are logical groupings of fields. By default, sections are rendered as tabs at the bottom of a form. The use of sections prevents users from having to scroll through long forms. Using a script, sections can be hidden when they are not needed.
Question: When you update a record, what happens?
Answer: It updates the existing record, and closes the form.
Question: What happens when you insert and stay?
Answer: It creates a new record and keeps the form open.
Question: What happens when you insert into a record?
Answer: It creates a new record and closes the form.
Question: When you save a record, what happens?
Answer: It updates an existing record, and keeps the form open.
Question: What’s the difference between the Save button and Update button?
Answer: With Save, the user remains on the same record and with Update, the user returns to the previously viewed record.
Question: When updating a form, which two options will return you to the previously viewed page?
Answer: Clicking Submit or Update will save your changes and return to the previously viewed page.
Question: How do you save a form, and stay in the current form view?
Answer: Right-click the form header and select Save to save changes without leaving form view.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-forms/task/t_EditingInForms.html
Question: What is a View in Forms?
Answer: A view is a different layout for presentation of a record’s data. Distinct user profiles have different views to see data from the same record. ServiceNow has a special view called the Self Service view. Self Service users do not require a ServiceNow license in order to see a record’s form. The view name appears on a form’s header. If there is no view name in the form header, the view is the Default view.
Question: How do you change views?
Answer: Click the additional actions menu and select the View menu item, then select a view.
Question: What are two ways to save forms?
Answer:
- By right clicking the form header
- Clicking the Context Menu (Hamburger Icon)
Question: Some forms have annotations. What are annotations?
Answer: Annotations are additional information on a form intended to provide on-screen instruction to users. Annotations have dark text on a colored background. Individual users can toggle annotations on and off.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-forms/concept/c_UsingForms.html
Question: Some forms have annotations. What are annotations?
Answer: Annotations are additional information on a form intended to provide on-screen instruction to users. Annotations have dark text on a colored background. Individual users can toggle annotations on and off.
Question: How do you personalize a form?
Answer: Click the Personalize Form icon.
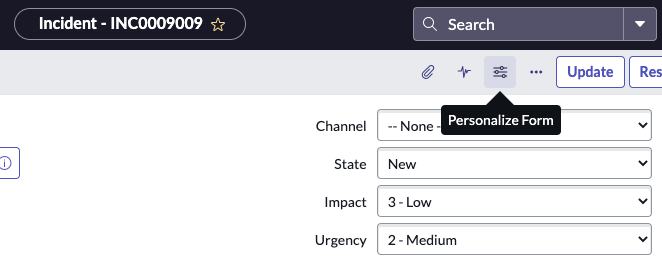
Question: What role is required to personalize a form?
Answer: Either the itil, personalize_form, or admin role is required.
Question: When you personalize a form, does the personalization apply globally, for all users?
Answer: No, that would be accomplished by customizing a form using the Form Builder application.
Question: How do you customize a Form?
Answer: Open a Form, Click the Context Menu (Additional Actions) > Configure > Form Layout
Configure > Form Layout
The Slushbucket will then appear, allowing you to customize the Form.
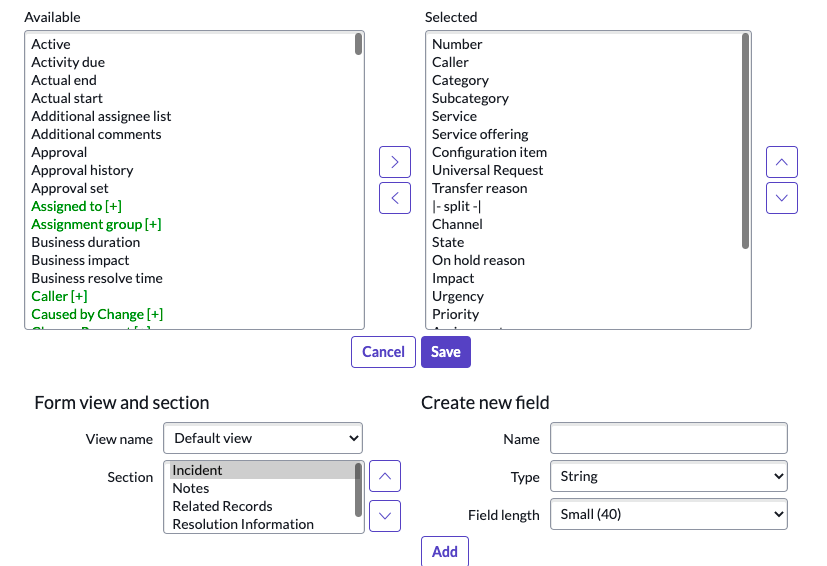
Form Context Menu
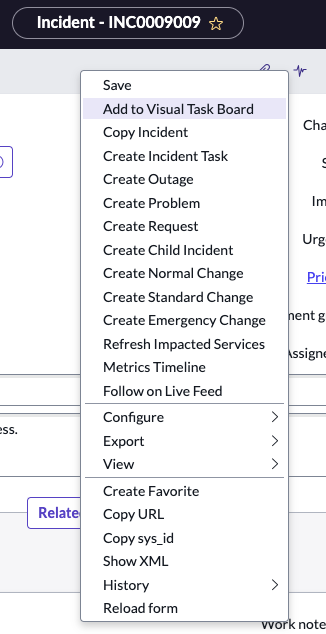
Question: What is the form context menu?
Answer:
The form context menu provides controls based on the table and user access rights. Administrators can customize some of the options available on a context menu using UI actions.
Question: How do you access the form context menu?
Answer: Access the form context menu by clicking an icon beside the form title or by right-clicking the form header
This is the context menu ( )
)
The light blue bar that runs the width of the content pane is the form header.

Options presented after right-clicking the form header:
Form Designer
Question: What can you do with Form Designer?
Answer: Administrators or users with the personalize_form role can use the form design feature to quickly create new or change existing form views.
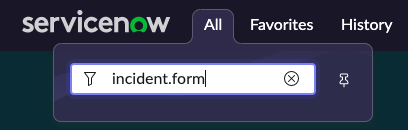
Question: How do you open the Form Designer?
Answer:
Type incident.form in the All menu to open a new form.
Now click the Additional Actions / Context Menu.

Select Configure > Form Layout
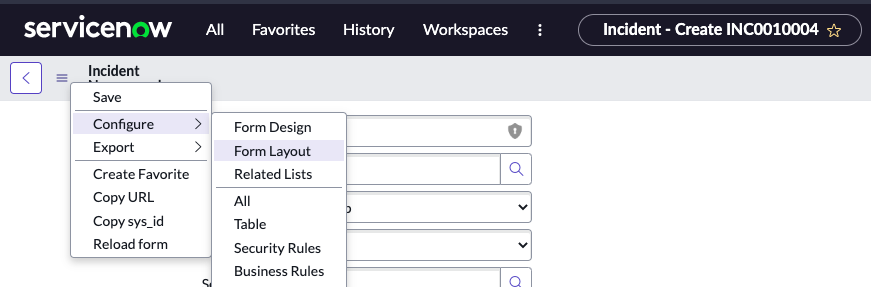
Question: What are the main components of the form design interface?
Answer: Page header, field navigator, and form layout.
G
Global Domain
Question: In the Global Domain, what are users allowed?
Answer: All users can see and manage records with permission, all users have access, and all users can potentially see records.
Global Search Filter
Question: What does the Global Search Filter do?
Answer: Helps you search across your instance for any related items most relevant to you.
Question: Where would you find Global Search?
Answer: In the Banner Frame.
If you use Global Search to look up “automatic replies outlook” for example, ServiceNow provides a link to a Knowledge base article on how to set up auto replies when you’re out of the office on vacation or otherwise.
Knowledge Article Out of Office Outlook
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/search-administration/concept/c_GlobalTextSearch.html
Question: What does Global Search allow you to do?
Answer: Global Search allows you to search multiple record types from a single search field.
Question: How do you perform a search?
Answer: You would perform one of the following actions based on your UI version: If you are using the Next Experience UI, you would enter your search terms in the Unified Navigation search field, then select View results or press Enter. If you’re using UI 16, Select the search icon in the banner on the upper right of the System settings for the user interface (UI) , then enter your search terms and press Enter.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/search-administration/concept/c_GlobalTextSearch.html
Groups
Question: What is the definition of Group in relation to access control?
Answer: A group is a set of users who share a common purpose. Members of groups perform similar tasks or need access to similar information for various purposes, such as approving change requests, resolving incidents, receiving email notifications, or administering the Service Catalog. Users working in ServiceNow are typically assigned to one or more groups. A group is a record in the sys_user_group table. Groups may inherit other groups. https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/users-and-groups/concept/c_Groups.html
Question: How do you create a User Group and assign roles to the Group?
Answer: Navigate to User Administration > Groups and create a new record (see table for field descriptions). To see some of the fields, you may need to Personalize a form.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/users-and-groups/task/t_CreateAGroup.html
Question: Do users assigned to the Group inherit the Group’s roles?
Answer: Yes.
GUID Globally Unique Identifier
Question: What is another name for the GUID?
Answer: sys_id
Question: What is the GUID, also known as the sys_id?
Answer: It is a Globally Unique Identifier 32-character hexadecimal string. Every record has a sys_id, and they are automatically generated for all records. Think of them like a barcode for identification. Every incident, problem, change, CI, KB article, they are all assigned a sys_id.
Hamburger Icon (List Controls)
Question: What is the hamburger icon called in the upper left when working with Lists?
Answer: The List Controls icon.
History
Question: What types of content display in the History menu?
Answer: Lists, records, and homepages.
Question: What does not appear in the History?
Answer: UI Pages and other non-standard interfaces.
Question: How is History organized?
Answer: Chronologically.
Question: By default, the History menu shows how many past history entries?
Answer: 30.
Homepage
Question: What is a homepage?
Answer: A homepage is a ServiceNow interface that consists of navigational elements, functional controls, and system information. Responsive and non-responsive dashboards provide a similar interface with additional functionality.When a user logs into an instance, the default homepage defined for their role appears, unless the user has switched to a different homepage. Administrators can customize several settings for homepages, including settings that control read or write access for any homepage and how homepages render.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/rome-platform-user-interface/page/administer/homepage-administration/concept/c_HomepageAdministration.html
Question: What determines which homepage a user will see after logging in?
Answer: Three things determine what you will see, depending on the following:
• If you personalized your homepage, the personalized homepage appears.
• If you did not personalize your homepage, the homepage for your role, such as admin or itil, appears. The homepage with the lowest Order value of the pages they have roles to see appears.
• If your role has no homepage, a blank page appears.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/rome-platform-user-interface/page/administer/homepage-administration/task/t_ViewYourHomepage.html
I
Import Sets and Importing Data
Question: What is the primary application used to load data into ServiceNow?
Answer: System Import Sets.
https://developer.servicenow.com/dev.do#!/learn/courses/sandiego/app_store_learnv2_importingdata_sandiego_importing_data_into_servicenow/app_store_learnv2_importingdata_sandiego_importing_data/app_store_learnv2_importingdata_sandiego_importing_data_objectives
Question: Where can you import data from with Import Sets?
Answer:
- A local source file (XML, CSV, Excel)
- A network server by providing a path and authentication information
- An LDAP connection
- A JDBC connection
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/import-sets/reference/import-sets-landing-page.html
Importing Data Into ServiceNow
Question: What does the Execution Contexts feature allow you to identify?
Answer: The Execution Contexts feature enables you to identify the order of execution of concurrent import sets. You can also open the import set records to access the import log.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/import-sets/task/monitor-sched-import-executions.html
Question: With a set of fields coalesced during import, what happens if an existing record with a matching value is found?
Answer: If an existing record with a matching value in the target table is found, that record is updated. If no matching record is found, then a new record is created in the target table.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/import-sets/concept/c_ImportSetCoalesce.html
Question: What is a Field Map?
Answer: Field maps create a reference between the data source columns and transaction columns.
Question: What is an Import Set Table?
Answer: A staging area for imported records.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/import-sets/reference/r_StandardImportSetTables.html
Question: What is captured in Update Sets?
Answer: Fields, Client Scripts, and Business Rules.
Question: What changes require special handlers?
Answer: Some changes require special handlers because they represent information on multiple tables. These changes are packaged into one update set entry so that all records are properly updated when the customization is committed. The following changes are tracked with special handlers:
• Workflows
• Form sections
• Lists
• Related lists
• Choice lists
• System dictionary entries
• Field labels
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/system-update-sets/reference/customizations-tracked-update-sets.html
Question: What are the four major steps to importing data?
Answer:
- Load data into a staging table.
- Create a Transform Map.
- Run a Transform to move data from the staging table to the target table.
- Check the data integrity.
Question: What is the first step to importing data?
Answer: Load data.
Question: How do you load data into an Import Set?
Answer: Navigate to All > System Import Sets > Load Data. The configuration options vary depending on the Data Source. In the example, the Data Source is an Excel file. The staging table, u_occasions_staging, is created dynamically.
https://developer.servicenow.com/dev.do#!/learn/learning-plans/sandiego/new_to_servicenow/app_store_learnv2_importingdata_sandiego_load_data
Question: True or False? The Import Set table acts as a staging table, but the data ultimately gets stored somewhere else.
Answer: True.
Question: True or False? Any user can manage and setup Import Sets?
Answer: False.
Question: What is the Mapping Assist utility?
Answer: The mapping assist utility provides a visually intuitive environment for specifying mapping between import set fields and production table fields. The mapping assist utility makes it possible to map a single source field (field on an import set table) to multiple destination fields (fields on a production table).
Question: When using the Load Data and Transform Map processes, what is Mapping Assist used for?
Answer: Mapping fields using a Field Map.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/script/server-scripting/concept/c_MappingOptions.html
Question: How do you load data from a data source into a staging table?
Answer: All > System Import Sets > Load Data.
Question: What are the steps to apply an update set to an instance or commit an update set?
Answer: Retrieve, preview, and commit.
Inbound Email Actions
Question: What are Inbound Email Actions?
Answer: Inbound email actions are similar to business rules: both use conditions and scripts that take action on a target table. An inbound email action checks the email for a watermark that associates it with a task and checks for other conditions. If the conditions are met, the system takes the inbound email action that you configure. The system can take two types of actions:
• Record action: setting a value for a field in the target table.
• Email reply: sending an email back to the source that triggered the action.
By default, if an email has no identifiable watermark, an inbound email action attempts to create an incident from the message. If the email has a watermark of an existing incident, an inbound email action updates the existing incident according to the action’s script.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/notification/concept/c_InboundEmailActions.html
Incident and Incident Management
Question: What is incident Management?
Answer: Incident Management restores normal service operation while minimizing impact to business operations and maintaining quality.
ServiceNow Incident Management supports the incident management process in the following ways:
• Log incidents in the instance or by sending email.
• Classify incidents by impact and urgency to prioritize work.
• Assign to appropriate groups for quick resolution.
• Escalate as necessary for further investigation.
• Resolve the incident and notify the user who logged it.
• Use reports to monitor, track, and analyze service levels and improvement.
Any user can record an incident and track it through the entire incident life cycle until service is restored and the issue is resolved.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/incident-management/concept/c_IncidentManagement.html
Question: What causes a high percentage of incidents?
Answer: Failed changes.
Question: What happens when a VIP caller calls in an incident?
Answer: The color of the caller’s name will change automatically. When a caller is assigned to an incident, the user record is automatically checked for VIP status. If the caller is a VIP caller, the VIP icon appears beside the caller name in the list view or the caller field in the form view.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/incident-management/task/t_FlaggingVIPs.html
Question: When you copy an Incident, what happens?
Answer: A new record is created, and the existing form is kept open.
Question: Where do you go to manage incident numbering?
Answer: Number Maintenance. Navigate to All > System Definition > Number Maintenance.
Question: How do you get to incident list view?
Answer: By typing incident.list
Question: Which table does the Incident table extend?
Answer: The task table.
Question: How do you enable the display of incident special handling notes? (Role required: admin)
Answer: You need to activate the Special Handling Notes plugin (com.sn_shn) to add the Create Special Handling Notes related link from which you can create the notes. After activation, the procedure is:
- Navigate to Incident > All
- Open any incident record.
- Click the Additional actions icon and select Configure > Form Layout
- From the Available list, select Special Handling Notes Pop Up and move it to the Selected list.
- Click Save.
- The Incident form can now display special handling notes.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/rome-it-service-management/page/product/incident-management/task/create-special-handling-notes.html
Question: What UI Actions are available from the context menu of the incident?
Answer: Copy the incident, create a request, create a problem, create a child incident, create a normal, standard, or emergency change.
Instance Appearance
Question: How do you customize instance appearance?
Answer: System Properties > CSS
Question: What can you change in terms of instance appearance?
Answer:
• Banner text color
• Banner and list caption background color
• Font used in forms and lists (this is a global font setting)
• Button styles (background color, border color, border width, text color)
• Field status indicator colors (including the indicators for Changed, Mandatory Populated, Mandatory Unpopulated, and Read-only)
• List cell vertical alignment
• Navigator menu styles (text font size, background color, text color)
• Header font name and size
• List and form caption color override
• Global text search background color (both for catalog results and knowledge base results)
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/administer/navigation-and-ui/reference/customizing-instance-appearance.html
Integration and Integration Hub Spokes
Question: Name a few standard integrations in ServiceNow:
Answer:
- Login (Single Sign-on) https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/integrate/single-sign-on/concept/c_MultipleProviderSingleSignOn.html
- LDAP https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/integrate/ldap/concept/c_LDAPIntegration.html
- Communications (Microsoft Teams is an example). https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/integrationhub/reference/microsoft-teams-spoke.html
- Monitoring
- Systems Management
https://www.servicenow.com/content/dam/servicenow-assets/public/en-us/doc-type/legal/snc-addendum-integrationhub.pdf
To see a list of Integration Hub Spokes: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/integrationhub/reference/spokes-list.html
Question: What are the most common processes required for integration with ServiceNow?
Answer: 1) CMDB 2) Incident Management 3) Problem Management 4) Change Management 5) User Administration 6) Single Sign-On
Question: What can be used to integrate Flow Designer with other instances and 3rd party applications?
Answer: Integration Hub.
ITIL Dashboard
Question: What is the ITIL dashboard?
Answer: The dashboard where you view, maintain, and track the tasks and incidents for operating the IT service desk.
Question: How do you access the ITIL dashboard?
Answer: To access the ITIL dashboard, navigate to:
1) All > Self-Service > Dashboards.
2) From All > Self Service > ITIL Dashboard > My Groups Work
3) From the Dashboards Overview, search for ITIL dashboard.
Question: Where can you see My Groups Work?
Answer: In the ITIL Dashboard.
Question: What does My Groups Work show you?
Answer: The outstanding work load (tasks) of the logged-in user’s group.
Question: What does My Work show you?
Answer: The logged-in user’s outstanding work load (tasks).
Question: What reports are available in the ITIL Dashboard?
Answer:
1) Critical Tasks – Total number of open critical task records for which Priority is set to 1.
2) Unassigned Tasks – The total number of open tasks that are still not assigned.
3) Tasks assigned to me – Total number of tasks assigned to the logged-user of the dashboard.
4) Active Incidents older than 7 days – Total number of active incidents logged before seven days ago.
5) Incident SLA Breached – Total number of incidents that exceed its SLA.
6) Incident SLAs at Risk – Total number of active incidents that have not yet exceeded an SLA but have elapsed 75% of the duration of the SLA.
7) My Groups Work – Outstanding work load (tasks) of the logged-in user’s group.
Question: Which module displays a list of tasks assigned to a user’s group, but not yet assigned to an individual user ?
Answer: The My Groups Work module. My Work shows the logged-in user’s outstanding work load (tasks).
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/use/dashboards/application-content-packs/itil-dashboard.html
K
Knowledge Bases and Knowledge Management
Question: What does the ServiceNow Knowledge Management (KM) application enable?
Answer: The Knowledge Management (KM) application enables the sharing of information (technical or non-technical) in knowledge bases. These knowledge bases contain articles that provide users with information such as self-help, troubleshooting, and task resolution.
Question: By default, who can create and edit categories in Knowledge?
Answer: Knowledge Contributors and Knowledge Managers.
Question: If a knowledge base has no access details specified, what users can read articles in that knowledge base?
Answer: Any active user can read articles.
Question: What determines which users can create, read, write, and retire knowledge articles?
Answer: User criteria.
Question: What options are there to control access to Knowledge bases through user criteria?
Answer: Can Read, Cannot Read, Can Contribute, Cannot Contribute.
Question: How do you add user criteria to the Knowledge base?
Answer: Navigate to All > Knowledge > Administration > Knowledge Bases.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/task/t_SelectUserCriteria.html
Question: What are the four knowledge workflows available in the ServiceNow base instance?
Answer:
A . Knowledge Approval Publish. Requests approval from a manager of the knowledge base. Articles in approval are In Review state before moving to Published state once approved or to Scheduled for publish if set to publish later. If the manager rejects the request, the workflow is canceled and the article remains in Draft state.
B. Knowledge Approval Retire. Requests approval from a manager of the knowledge base before moving the article to the retired state. The workflow is canceled and the article remains in the published state if any manager rejects the request.If ownership groups is enabled, email notifications with a link to the article are sent to the ownership group members for approval.
C . Knowledge Instant Publish. Immediately publishes a draft article without requiring an approval, or publishes on the scheduled publish date if set to publish later.
D . Knowledge – Instant Retire. Immediately retires a published article without requiring an approval.
E . Knowledge – Publish Knowledge. A subflow that moves the knowledge article to the published state. You can use this subflow when defining your own workflow.
F . Knowledge – Retire Knowledge. A subflow that moves the knowledge article to the retired state. You can use this subflow when defining your own workflow.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/reference/r_KnowledgeWorkflows.html
Question: What are some of the most common methods of populating knowledge bases?
Answer: Copying/pasting articles, importing HTML, and creating them from scratch in ServiceNow.
Question: True or False? There are OOTB (out-of-the-box) workflows and you can also create your own.
Answer: True.
Question: Does Knowledge Management support multiple Knowledge bases?
Answer: Yes.
Question: When can a Knowledge article be seen?
Answer: After it is published.
Question: How are articles grouped in the Knowledge base?
Answer: By category.
Question: Knowledge base search results can be sorted by which three things?
Answer: Relevancy, Last Update, and Number of views.
Question: What is the KB News Widget used for?
Answer: To display important news and information from the Knowledge Base, like email service interruption during routine maintenance, or announcements of upcoming events. You can use this base system widget as-is in your portal or clone it to suit your own business needs. You configure the KB News widget to display specific information by selecting a category from the KB category list.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/build/service-portal/concept/kb-news-widget.html
Question: What are some of the options to filter by when working with Knowledge?
Answer: Filter by Knowledge base name, category, author, resource, rating, last modified, and view count. https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/task/enable-search-on-all-kb.html
Question: What are two methods of accessing the knowledge bases?
Answer: Through the Service Portal (by appending /sp to your instance URL), and through the Platform UI (Filter Navigator).
Question: How do most people access the Knowledge Portal?
Answer: Through the Service Portal (append /sp to your instance name).
Question: Knowledge categories can be created and edited by which two roles?
Answer: 1) Knowledge Manager 2) Knowledge Admin
Question: Which role is required to manage more than one knowledge base?
Answer: knowledge_admin
Question: What is the sequencing of publishing a knowledge article?
Answer: Draft > Review > Publish > Retire
Question: A Knowledge article must be in which State to be displayed to a user?
Answer: Published.
Question: What are three ways an end user can leave feedback about an article?
Answer:
- Give it a 1-5 star rating
- Mark the article as helpful or not helpful
- Leave a comment on the article
- Question: How many ways are there to submit feedback on a Knowledge article? What are they?
Answer: 4.
1) Flag an article as incorrect or inappropriate.
2) Provide a rating value for the article.
3) Mark an article as helpful or not helpful.
4) View comments, add a new comment, or reply to existing comments.
Question: How many ways are there to submit feedback on a Knowledge article? What are they?
Answer: 4 ways:
1) Flag an article as incorrect or inappropriate.
2) Provide a rating value for the article.
3) Mark an article as helpful or not helpful.
4) View comments, add a new comment, or reply to existing comments.
Question: How do you view feedback on Knowledge articles?
Answer: Users can view comments directly on the article. Knowledge managers can view the other types of feedback by navigating to Knowledge > Feedback.
Question: How do you disable or configure feedback?
Answer: Administrators and knowledge managers can disable some feedback options using fields on the Knowledge Base form. Administrators can configure feedback options using properties.
Question: How do you flag articles?
Answer: Click Flag Article in the article header to open a new window, allowing you to enter suggested changes.
Question: Do flagged articles appear on the Article View page?
Answer: No. Flagged comments do not appear on the Article View page. Users with the admin, knowledge_admin, and knowledge_manager roles can access flagged articles by navigating to Knowledge > Articles > All Flagged. Users with the knowledge role can access their flagged articles by navigating to Knowledge > Articles > My Flagged. If disabled, the author of the article and users with the admin, knowledge_admin, and knowledge_manager roles can see all flagged comments. Other users can see only their own flagged comments.
Question: How do mark a knowledge article that should be reviewed?
Answer: Flag article.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/reference/r_KnowledgeFeedback.html
Question: Which feature allows end users to post questions and answer other user questions?
Answer: Social Q&A
Question: What is the best way to share a knowledge article with another user?
Answer: A permalink
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/concept/knowledge-service-portal-view.html
Question: What item in the Knowledge Management Service Portal displays articles that have the highest percentage of users marking them helpful?
Answer: Most Useful.
Question: How do you create a Knowledge base?
Answer: Navigate to All > Knowledge > Administration > Knowledge bases. Click New.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/task/create-a-knowledgebase.html
Question: Name three methods of populating a knowledge base with knowledge articles:
Answer:
1) Creating articles directly in the ServiceNow Platform
2) Importing Microsoft Word files
3) Integrating with a WebDAV compliant source
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/task/use-knowledge-management.html
Question: What are three ways of creating Knowledge articles?
Answer:
• Navigate to Self-Service > Knowledge and click the Create an Article icon.
• Navigate to Knowledge > Articles > Create New
• From the Knowledge Management homepage, click the more icon () and then select Create Article.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/task/create-knowledge-article.html
Question: What is a Knowledge Block?
Answer: Reusable pieces of content secured by user criteria that you can add to knowledge articles in a knowledge base. The user criteria controls which users can read or not read the block content in an article or search, enabling users to more easily view content that is relevant to them. Knowledge blocks are available for use in Now Platform only.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/concept/knowledge-blocks.html
Question: How do you add a knowledge block to a knowledge article in Agent Workspace?
Answer:
- Navigate to All > Agent Workspace > Agent Workspace Home
- Go to Lists > Knowledge Articles > All
- Click an existing article link.
Known Errors
Question: How do you create a Known Error?
Answer:
- Navigate to All > Problem > Open
- Open the Problem record.
- Under Related Links, click Create Known Error Article.
L
LDAP Integration
Question: What does LDAP integration allow you to do?
Answer: An LDAP integration allows your instance to use your existing LDAP server as the primary source of user data.
Question: Do user passwords import into ServiceNow with LDAP integration?
Answer: No, the password that the user enters is contained entirely in the HTTPS session. The integration never stores LDAP passwords.
Question: Does the integration write to the LDAP directory?
Answer: No, the integration uses a read-only connection that never writes to the LDAP directory. The integration only queries for information, and then updates its internal database accordingly.
Question: What are the LDAP Integration features?
Answer:
1) Scheduled LDAP refresh
2) LDAP listener
3) On-demand LDAP login
4) LDAP data population
5) LDAP authentication
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/integrate/ldap/concept/c_LDAPIntegration.html
Lists
Question: What is a list?
Answer: A list is a content page displaying zero or more records from the same table. Rows and columns organize the list. Each row is a record and each column is a field from the record.
Lists are:
• Searchable – Enter a value in the Search field
• Sortable – Click the column label
• Editable (if permissions allow): Double-click a field value
https://developer.servicenow.com/dev.do#!/learn/courses/sandiego/app_store_learnv2_buildmyfirstapp_sandiego_build_my_first_application/app_store_learnv2_buildmyfirstapp_sandiego_servicenow_basics/app_store_learnv2_buildmyfirstapp_sandiego_lists
Question: What displays a set of records from a table?
Answer: A list.
Question: What are the components of the list user interface?
Answer: Title Bar, Breadcrumbs, Column Headings, Column Header Search, Field Values
Question: How do you personalize list columns?
Answer: Click the gear icon.
Once you click the gear icon to personalize the list, and the slushbucket menu will appear.
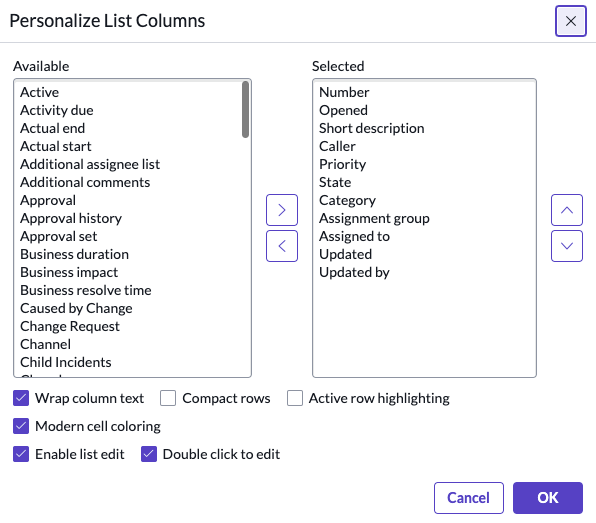
Question: What is another way to personalize a list?
Answer: Click Column Options > Configure > List Layout
Click Column Options (the ellipsis)
Then Configure > List Layout
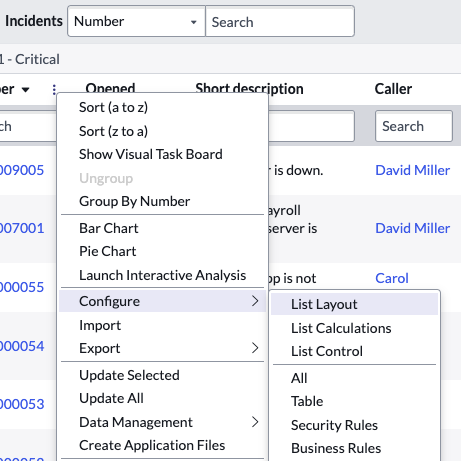
Question: If you’ve personalized a list, what will you see in the title bar?
Answer: A tiny dot on the Gear icon.

Question: When you modify the list view of a specific list in ServiceNow for everyone, what’s it called?
Answer: Configuring the list.
Question: How do you configure the List Layout?
Answer: Open the list title menu in the upper left corner and select Change View, and then click the name of the view.
Click the List Title Menu
Then View > Select the View
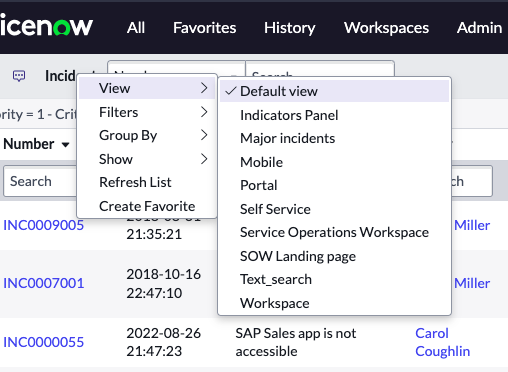
Question: Can users configure the list layout for themselves?
Answer: Yes.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/list-administration/task/t_ConfigureTheListLayout.html
Question: True or false? Resetting the list layout globally will override personal preferences.
Answer: False.
Question: What role is required to configure lists globally (system wide)?
Answer: The System Administrator role.
Question: What can you do with List Configuration?
Answer: With list configuration, you can add, remove, and reorder list columns. You can configure calculations to appear under columns. You can also hide controls and define access conditions by role for existing list controls. Configuring lists is called personalizing lists in versions prior to the Fuji release.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/list-administration/concept/c_ListConfiguration.html
Question: How do you edit a field value within a list?
Answer: Double click in the field.
Question: Are searches in lists case sensitive?
Answer: No. Searches in lists are not case sensitive.
Question: How do you change the sort sequence for lists?
Answer: By modifying the order field.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/list-administration/concept/c_ControlTheListSortSequence.html
List Controls Icon (Hamburger Icon)
Question: What is the hamburger icon called in the upper left when working with Lists?
Answer: The List Controls icon.
Question: How do you add the current filtered list to your Favorites?
Answer: The List Controls icon > Favorites. You can then choose your Favorite icon color and name the Favorite.
List Edits
Question: What are the various methods to edit lists?
Answer:
1) Quick edit functions. To edit a record in a list using quick edit functions, right-click a field and select the appropriate function.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/reference/r_MethodsForListEdits.html
2) The List Editor. The list editor lets you edit field values in a list without opening a form. Administrators can configure the list editor. By default, list editing is disabled for some tables. Fields of certain types cannot be edited from lists.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/reference/r_MethodsForListEdits.html
List Editor
Question: What does the List Editor allow you to do?
Answer: The list editor allows you to edit field values directly from a list without navigating to a form.
Question: Can you edit multiple fields in the same column at the same time?
Answer: Yes. To select multiple fields in the same column, hold Shift and press the Down Arrow or the Up Arrow key.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/tokyo-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/task/t_EditMultRecUsingListEditor.html
Question: What are the two ways users enter data into a Field?
Answer: By using the list editor or by using a form. In form view, fields appear as fields in the form, and in list view they appear as columns of data in the table.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/task/t_UseTheListEditor.html
M
Maintain Items
Question: Which module do you access within the Service Catalog application to create a new Catalog Item ?
Answer: The Maintain Items module.
Question: How do you access the Maintain Items module to add a new Catalog Item?
Answer: All > Service Catalog > Catalog Definitions > Maintain Items
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/task/t_DefineACatalogItem.html#t_DefineACatalogItem
Metrics and Metric Definitions
Question: What is a metric?
Answer: A metric measures and evaluates the effectiveness of IT service management and organizational processes. A metric or a combination of metrics can provide an insight into a system, component, or process.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/use/reporting/concept/c_MetricDefinitionSupport.html
Modules
Question: Where are Modules nested?
Answer: Modules are nested under Applications when you search for that Application in the Filter Navigator. For instance, under the Service Portal Application are the following Modules:
Portals Announcements Agent Chat, and more.
N
Navigation Menus
Question: Which elements are included in the Navigation Menu?
Answer: All, Favorites, History, and Workspaces
Next Experience Unified Navigation
Question: Where in the Next Experience Unified Navigation does Global Search appear?
Answer: In the Banner Frame. In this case, the search is by Incident number.
Question: Where in the Next Experience Unified Navigation does the Help icon appear?
Answer: In the Banner Frame.
Question: Where in the Next Experience Unified Navigation does the Contextual App Pill appear?
Answer: In the Banner Frame.
Question: Where in the Next Experience Unified Navigation do you access All (applications and modules)?
Answer: In the All Menus.
https://docs.servicenow.com/en-US/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/get-started/servicenow-overview/concept/using-the-next-experience-global-header.html
Notifications
Question: What are the 3 types of notifications?
Answer: Email, Push, and Provider
Question: What are Notifications used for?
Answer: You use Notifications to notify users about specific activities in ServiceNow, such as updates to incidents or change requests.
Question: What do Notifications allow administrators to specify?
Answer:
- When to send the notification
- Who receives the notification
- What content is in the notification
Question: How do you access base system notifications?
Answer: To see what base system notifications are available as an administrator, navigate to System Notifications > Email > Notifications. Once you click on Notifications, you see a list of available base system notification options.
Question: How can you prevent users from feeling overwhelmed by Notifications?
Answer: Through making notifications subscribe-able, and using Email Digest.
Question: What is Email Digest?
Answer: a single email that summarizes the activity for a selected notification and its target record during a specified time interval.
Question: Where do you override the Notification message HTML?
Answer: On the what it will contain tab.
Question: Where do you select variable values to include in Subject or the body of the message?
Answer: On the what it will contain tab.
Question: Where do you define conditions to be met to send notifications?
Answer: On the when to send tab.
Question: How do you identify if a record insert or update results in the notification?
Answer: On the when to send tab.
Question: What do system address filters prevent?
Answer: System address filters prevent your system from communicating with untrusted domains and email addresses.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/notification/concept/system-address-filters.html
Now Experience UI Framework
Question: What is the Now Experience UI Framework?
Answer: A ServiceNow JavaScript framework for creating web components.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/paris-application-development/page/build/components/concept/custom-components.html
Now Mobile App
Question: The Now Mobile App is targeted towards which role?
Answer: The Fulfiller role.
Question: The Now Mobile App is targeted to which person?
Answer: The employee. It includes functionality such as reporting broken items and finding available conference rooms.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-employee-service-management/page/administer/mobile-employee/concept/mobile-employee-experience.html
Now Platform UI and Interfaces
Question: What are the three Now Platform interfaces?
Answer:
1) Next Experience Unified Navigation
2) Now Mobile App
3) Service Portal
Question: What is the primary way users interact with applications and data in ServiceNow?
Answer: Through the Now Platform UI
Number Maintenance
Question: Where do you go to manage incident numbering?
Answer: Number Maintenance. Navigate to All > System Definition > Number Maintenance.
O
Order Guides
Question: What are Order Guides?
Answer: Order Guides allow users to order everything they need (multiple items) in one request. For example, a New Employee Hire order guide can contain several items that new employees commonly need, such as business cards, computer, and cell phone. After selecting this order guide, the customer can then provide information about the new employee, including location and job title. The order guide then submits an order for catalog items like business cards, based on the details provided. https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_ServiceCatalogOrderGuides.html
P
Performance Analytics
Question: What is Performance Analytics?
Answer: ServiceNow® Performance Analytics is an in-platform process optimization solution to create management dashboards, report on KPIs and metrics, and answer key business questions to help increase quality and reduce the costs of service delivery.
Question: How can you to track and aggregate data over time through elements called scorecards and indicators ?
Answer: With Performance Analytics
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/use/performance-analytics/reference/r_PALandingPage.html
Question: What are Performance Analytics Indicators?
Answer: Indicators define a performance measurement taken at regular intervals of a business service, an activity, or organizational behavior. These performance measurements result in a series of indicator scores over time.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/use/performance-analytics/concept/c_Indicators.html
Question: What are Performance Analytics Breakdowns?
Answer: Breakdowns enable you to group or filter indicator scores by a qualitative attribute such as Priority, Category, or Assignment Group. You can apply a breakdown on the Analytics Hub, in KPI Details, and on dashboards.The values for each breakdown are called breakdown elements. For example, the Priority breakdown may have the elements Critical, High, and Low. Breakdowns are categorized as automated, manual, or external, depending on where these elements come from. Automated breakdown elements are specified in breakdown sources. Manual breakdowns have their elements entered manually to define an organization. Lastly, an external breakdown specifies the JDBC data source and SQL statement for retrieving breakdown elements.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/use/performance-analytics/concept/c_CreatingBreakdowns.html
Pin Menus
Question: As an end user, what can you use to maximize your working space?
Answer: Pin menus.
Platform Architecture
Question: The Now Platform is an example of which cloud computing model?
Answer: Application Platform-as-a-Service, or aPaaS.
Question: What is the definition of server?
Answer: A server is a computer program or device that provides a service to another computer program and its user, also known as the client. In a data center, the physical computer that a server program runs on is also frequently referred to as a server. That machine might be a dedicated server or it might be used for other purposes.
In the client / server programming model, a server program awaits and fulfills requests from client programs, which might be running in the same, or other computers. A given application in a computer might function as a client with requests for services from other programs and as a server of requests from other programs.
Definition via Techtarget: https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/server
Question: How does ServiceNow store data?
Answer: In a relational database (MariaDB).
Question: ServiceNow is built upon which foundations?
Answer: ITIL, SaaS, PaaS, Web 2.0, IT 3.0
Platform Administration
Question: Where do you see information about platform activity?
Answer: System Logs.
Question: What do System Logs provide?
Answer: The System Logs module provides a variety of logs that you can use to troubleshoot and debug transactions and events that take place within the instance.
Question: How do you access Event Logs?
Answer: System Policy > Events > Event Logs
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/platform-events/event-logs-2.html
Question: How do you manage Record Numbering?
Answer: Administrators can manage record numbering by navigating to System Definition > Number Maintenance. The current number format for a table, including the prefix (such as INC for incidents or CHG for changes), is stored in a record on the Number [sys_number] table.
Question: If you want to change the prefix from INC to INCDT in record numbering, how would you do it?
Answer: Through Number Maintenance.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/field-administration/concept/c_ManagingRecordNumbering.html
Plugins
Question: How do you activate a Plugin?
Answer: Navigate to All > System Applications > All Available Applications > All. Find the plugin using the filter criteria and search bar.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/plugins/task/t_ActivateAPlugin.html
Predictive Intelligence
Question: What does Predictive Intelligence do to resolve requests faster?
Answer: It uses machine-learning algorithms to determine field values during record creation. Existing data records are required to “train” machine-learning to make effective decisions.
Question: Predictive Intelligence uses machine-learning algorithms to populate which fields:
Answer: 1) Category 2) Service 3) Priority 4) Assignment Group 5) Assigned To
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/administer/predictive-intelligence/concept/predictive-intelligence.html
Process Automation Designer
Question: What does Process Automation Designer allow you to do?
Answer: Process Automation Designer enables process owners to author cross-enterprise workflows and create a single, unified process. You can also use Process Automation Designer to provide end users with a simplified, task-oriented view of your process. You can organize Flow Designer content into unified and digitized cross-enterprise processes. With Process Automation Designer, you gain these benefits:
Problem Management
Question: What is a Problem?
Answer: A problem is a cause of one or more incidents. Create a problem to identify the root cause of the multiple related incidents, and try to prevent them from happening again. ITIL defines a problem as the cause of one or more incidents.
Question: What are the primary objectives of problem management?
Answer: To prevent problems and incidents from happening, eliminate recurring incidents, and to minimize the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented.
Question: What are the two methods to create a problem?
Answer:
1) From the Problem module: Navigate to Problem > Create New
2) From within an Incident record:
- Open the incident.
- On the context menu, click Create Problem. When you do so, use the property List of attributes (comma-separated) that will be copied from the incident to create a new problem (com.snc.problem.create_from_incident.attributes) to specify fields on the Incident form. The values of these fields are copied to the respective fields on the Problem form.
- See the documentation for the rest of the steps necessary:
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/problem-management/task/create-a-problem-v2.html
Question: What does Problem Management help you do? Answer:
Question: What does Problem Management help you do?
Answer: Problem Management helps to identify the cause of an error in the IT infrastructure, reported as occurrences of related incidents.
Problem Management is responsible for managing the life cycle of all problems and to prevent problems and resulting incidents from happening. It also aims at eliminating recurring incidents and minimizing the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented. Resolving a problem includes the activities required to diagnose the root cause of incidents and to determine the resolution for the problem. Problem resolution and elimination of root cause often calls for applying a change to the configuration item in the existing IT environment.
Problem Management also maintains information about problems and the appropriate workarounds and resolutions, so that the organization is able to reduce the number and impact of incidents over time. In this respect, Problem Management has a strong interface with Knowledge Management so that the known error articles are documented thoroughly for any future reference.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/problem-management/concept/c_ProblemManagement.html
Question: What are the Problem States?
Answer: New > Assess > Root Cause Analysis > Fix in Progress > Resolved > Closed
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/problem-management/task/resolve-and-complete-problem.html
Process Guide
Question: How do Process Guides work?
Answer: Process guides work similarly to approval rules in that their execution is controlled via a condition.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/service-administration/task/t_ProcessGuideApprovals.html
R
Records
Question: What are Records?
Answer: Records are data stored on tables, which contain fields. A record in ServiceNow is like a row in a spreadsheet, it is a single entity, and has a unique key, called a sys_id.
Question: What is the term used to describe all the data saved within a particular form?
Answer: A Record.
Question: What do forms display?
Answer: Forms display information from one record in a table.
Question: When you update a record, what happens?
Answer: It updates the existing record, and closes the form.
Question: A Record is a _ and a Column is a __ ?
Answer: Row and Field.
Question: How can you update multiple records at once?
Answer: With the List Editor, with the Update Multiple Records action (as a Flow Designer ServiceNow core action).
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/flow-designer/reference/update-multiple-records-flow-designer.html
Record Numbering
Question: How do you manage Record Numbering in ServiceNow?
Answer: Administrators can manage record numbering by navigating to System Definition > Number Maintenance. The current number format for a table, including the prefix (such as INC for incidents or CHG for changes), is stored in a record on the Number [sys_number] table.
Record Producer
Question: What is a Record Producer? Where are they stored?
Answer: A Record Producer is a specific type of Catalog Item that allows end users to create task-based records, such as Incident records, from the Service Catalog. They are a form that produces a task record, and are a type of Catalog Item. Records are produced and stored on tables outside of the Catalog space.
Question: What are three examples where a user would be directed to a Record Producer?
Answer: Password reset, report outage, and Create Incident.
Question: How do you create a Record Producer to log incidents directly from the Service Catalog? (catalog_admin or admin role is required).
Answer: Navigate to All > Service Catalog > Catalog Definitions > Record Producers, and follow the rest of these instructions:
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/incident-management/task/t_CreateARecordProducer.html
Question: Why would you use a Record Producer instead of a standard task-based form?
Answer: In order to provide a better end-user experience. The look and feel of a record producer is similar to that of a catalog item. But the record producer generates a task record such as incident, instead of a requested item.
Question: Should you create Requested Item records from Record Producers?
Answer: No, you would create a Requested Item using Catalog Items.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_RecordProducer.html
Reference Field
Question: What is a reference field?
Answer: A reference field stores a reference to a field on another table. For example, the Caller field on the Incident table is a reference to the User [sys_user] table. Another common example is the assignment group is a reference field to the groups table.
Related Lists
Question: What is a Related List?
Answer: Related lists appear on forms and show records in tables that have relationships to the current record. In other words, to present related records.
Users can view and modify information in related lists like any other list. Administrators can configure related lists to appear on forms and in hierarchical lists by configuring a form. Related lists do not have a size limit.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-forms/concept/c_RelatedLists.html
Question: How do you configure Related Lists?
Answer: Additional Actions / Context Menu > Configure > Related Lists

You will then see the slushbucket with choices for the Related List selected.
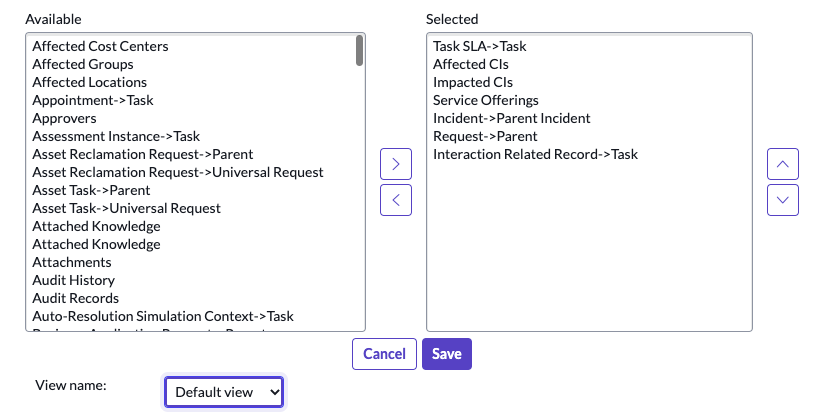
Reports and Reporting
Question: How do you create a report visualization?
Answer: If new, Navigate to Reports > Create New.
Question: How do you edit an existing report?
Answer: Navigate to Reports > View / Run and click the edit icon (the pencil) beside the report name.
Question: Where can you see My Groups Work?
Answer: From the ITIL Dashboard.
Question: How do you access the ITIL dashboard?
Answer: To access the ITIL dashboard, navigate to All > Self-Service > Dashboard. On the Dashboards Overview, search for ITIL dashboard.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/use/dashboards/application-content-packs/itil-dashboard.html
Question: What are two ways to create a report?
Answer:
1) Navigate to Reports > View / Run
2) From the List Column Heading
Question: How do you make a report accessible to external audiences using a URL?
Answer: Click the Publish button.
Question: How do you create a report on a Dashboard?
Answer: Navigate to the dashboard where you want to add the report, click the Add Widgets icon (The Plus sign), and select Reports.
Question: How do you edit a report on a Dashboard?
Answer: Navigate to the dashboard where the report resides and click Edit. To edit a report, click its edit icon (The pencil).
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/use/reporting/task/t_CreateYourOwnReport.html#t_CreateYourOwnReport
Question: In regards to ServiceNow reporting, what can a metric do?
Answer: Measure and evaluate the effectiveness of workflows and SLAs. https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/use/reporting/reference/reporting-landing-page.html
Question: How do you view how often each of your reports is run and how long it takes for the report to run? Answer: The Report Stats List allows you to see each.
Question: What is the recommended way to share a report?
Answer:
1) Share the Report.
2) Publish to an instance URL.
3) Download as a PDF.
4) Email as an attachment.
Question: After you create a report, where does it appear?
Answer: It appears in the All > Reports > View/Run module under the My reports list.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/use/reporting/reference/report-statistics.html
Question: What are two methods of viewing Instance Stats?
Answer:
- All > System Diagnostics > Stats > Stats
- In the Filter Navigator, type stats.do
Question: Reports can be created from which two places?
Answer: 1) The List Column heading 2) View / Run module
Question: What types of reports are available?
Answer: You can generate the following types of reports, organized by category:
• Bar reports enable you to compare scores across data dimensions.
• Pie and Donut reports visualize the relationship between the parts and the whole of a data set using shapes such as pies.
• Time Series reports visualize data over time. In addition to data from within your instances and imported data sources, you can also use MetricBase data in time series reports. For more information, see MetricBase application.
• Multidimensional reports visualize data across dimensions in a single table or graph.
• Scores visualize single data points either across ranges or as a single value.
• Statistical reports visualize data with statistical values such as medians and means.
• Other reports include calendars, maps, and lists.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/use/reporting/reference/report-types-creation-details-rd.html
Request
Question: When a user orders a catalog item, what is created?
Answer: A Request is created that follows a fulfillment process. A fulfillment process defines the steps to request approval, assign fulfillment tasks, and fulfill requests. Execution plans or workflows are used to define fulfillment processes.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/request-fulfillment.html
Question: What happens when a Request is rejected?
Answer: A notification is sent, and the status is set to rejected.
Question: What are the Request States?
Answer: Draft, Awaiting Qualification, Qualified, Awaiting Approal, Approved, Work In Progress, Closed Complete, Closed Incomplete, Canceled.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-service-management-for-the-enterprise/page/product/planning-and-policy/reference/r_SMRequestStates.html
Question: What is a Request Catalog?
Answer: A Request Catalog is a list of business and technical products, services, service commitment options, and offerings that you can order. Catalogs enable you to order and manage your available products and services. Catalogs (such as the Human Resources [HR] service catalog) help manage services that a user can access. Catalogs are the starting point for accessing available services, and contain catalog items.
Question: True or False? ServiceNow doesn’t recommend having a service for generic requests in the service catalog.
Answer: False. It is a best practice to offer a service for generic requests.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/csdm-implementation/concept/request-catalog.html
Request Management
Question: For request fulfillment processes, does ServiceNow recommend using Workflows, or an Execution Plan?
Answer: Workflows.
Question: What does the My Requests widget allow you to see in a single view?
Answer: Requesters can view open or closed requests in Service Portal. Requests, incidents, and tasks are displayed in a single view.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/build/service-portal/concept/my-request-widget-portal.html
Question: What is generated from the Service Catalog once a user places an order for an item or service?
Answer: A Request
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-field-service-management/page/product/planning-and-policy/concept/c_RequestManagement.html
Roles and Role Based Access Controls
Question: What do Roles allow you to do?
Answer: Roles control access to features and capabilities in applications and modules. The admin role provides access to all features and capabilities.
After access has been granted to a role, all the groups or users assigned to the role are granted the access. Roles can contain other roles, and any access granted to a role is granted to any role that contains it.
For a complete list of the roles included with the ServiceNow platform, see Base system roles.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/roles/concept/c_Roles.html
Question: Fill in the blank. A Role is a _
Answer: A collection of permissions.
Question: Fill in the blank. A Group is a _
Answer: Set of users who share a common purpose.
Question: What group of permissions is used to control access to Applications and Modules?
Answer: Roles
Question: Can roles contain other roles?
Answer: Yes. Roles can contain other roles, and any access granted to a role is granted to any role that contains it.
Question: In which table are roles stored?
Answer: A role is a record in the sys_user_role table.
Question: Which elevated role is required to modify access control rules?
Answer: security_admin
Question: Roles may be part of ______ number of access control rules?
Answer: One or more.
Question: Which role allows users to define catalog items?
Answer: catalog_admin
Question: What role do you need to create a new table?
Answer: The admin role.
Question: A group may contain _____ or more number of users?
Answer: Zero or more users.
Question: Which roles can impersonate another user?
Answer: The impersonator and admin roles can impersonate another user.
Question: Which are the most common out-of-the-box roles in ServiceNow?
Answer: ITIL, itil_admin, admin, security_admin, knowledge_admin, report_admin, catalog_admin, asset, ecmdb_admin, impersonator
Question: Which role can maintain user criteria?
Answer: user_criteria_admin
Question: What is the role required to create a UI Policy?
Answer: ui_policy_admin
Question: What roles are required for access to CMDB tables and underlying data?
Answer: asset, itil, itil_admin, and cmdb_read
Question: What is an Elevated Privilege role?
Answer: Elevated privilege roles require you to manually accept the responsibility of using the role before you can access the features of the role. By default, you do not have elevated privilege roles upon login. You must manually elevate to the privilege of the role. An elevated privilege role lasts only for the duration of your user session. Session timeout or logout removes the role. You can designate any role as an elevated privilege role, and then assign that role to one or more users. Do this when you want to restrict users from having access to the rights that the role provides immediately after login. You can designate the privilege role on the Role form. See Create a role for instructions.
To use an elevated role, you must meet these conditions:
• The elevated role must be assigned to you.
• You must manually elevate to a specific elevated role to get its privileges, even if you are already elevated to a second elevated role that contains the first elevated role.
For example, if elevated role A contains elevated role B, even if you elevate to role A, you must still elevate to role B to get its privileges.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/security/concept/c_ElevatedPrivilege.html
Question: What are Base Tables?
Answer: Tables that cannot be extended.
Question: How can you see a list of Base Tables in your instance?
Answer: Replace YOURINSTANCE with your instance name, and open that URL in a new browser tab while logged into your instance. https://YOURINSTANCE.service-now.com/sys_db_object_list.do?sysparm_query=super_class%3DNULL
Question: What can you find a list of Base System roles in the ServiceNow documentation?
Answer: Click here: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/roles/reference/r_BaseSystemRoles.html#r_BaseSystemRoles
Question: What are the details of the security_admin role?
Answer: The security_admin role is an elevated privilege role provided with High Security Settings that lets users create and change access controls and change High Security Settings. In the base system, only the default System Administrator (admin) user has the security_admin role. Since it requires elevating privileges, the admin user does not have this role at login. After elevating privileges, the admin user has the security_admin role for the duration of the user session.
Question: True or False? A user with the security_admin role can grant the security_admin role to other users?
Answer: True.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/security/concept/security-admin-role.html
Question: True or False? A user with the security_admin role can grant the security_admin role to other users?
Answer: True.
Question: What role does an IT Agent have?
Answer: The itil role. An IT Agent views, opens, updates, tracks, and closes incidents and tasks for managing customer issues.
Question: What role does an IT Agent Admin have?
Answer: The itil_admin role. ITIL Admins can perform all the activities of an IT agent, and in addition, the IT Agent Admin can also modify the data and layout.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/use/dashboards/application-content-packs/itil-dashboard.html
Question: What is true about fulfillers and approvers?
Answer:
1) Fulfillers have the itil role and the approver_user role.
2) Approver users only have the approver_user role, and not the itil role.
Question: When do you elevate a role? Who uses the feature typically?
Answer: Administrators use it when modifying high security settings.
Question: What is the preferred method of role management?
Answer: Every user belonging to a group inherits that group’s roles, so the preferred method of role management is:
1) Add users to a group
2) Apply roles to groups
When removing a user from a group, roles inherited by that group are revoked for that user. Similarly, a group may contain other groups, where a child group inherits all roles owned by its parent. Users added to child groups gain roles of that child group plus any parent groups.
Question: How are users related to groups?
Answer: In one-to-many relationships.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/roles/concept/c_Roles.html
Question: Knowledge categories can be created and edited by which two roles?
Answer: 1) Knowledge Manager 2) Knowledge Admin
Question: Which role is required to manage more than one knowledge base?
Answer: knowledge_admin
Question: By default, who can create and edit categories in the Knowledge?
Answer: Knowledge Contributors and Knowledge Managers.
Question: What options are there to control access to Knowledge bases through user criteria?
Answer: Can Read, Cannot Read, Can Contribute, Cannot Contribute.
Question: How do you add user criteria to the Knowledge base?
Answer: Navigate to All > Knowledge > Administration > Knowledge Bases.
Question: What is the minimum role needed to create Import Sets?
Answer: import_admin
Question: What role is required for creating user criteria for controlling access to knowledge bases and articles?
Answer: user_criteria_admin
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/task/create-user-criteria-record-in-knowledge-management.html
Question: What role must you have to configure forms using the Form Designer?
Answer: The admin or personalize form role.
Question: What does an LDAP integration allow you to do?
Answer: An LDAP integration allows your instance to use your existing LDAP server as the primary source of user data.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/integrate/ldap/concept/c_LDAPIntegration.html
Question: What does LDAP stand for?
Answer: Lightweight Directory Access Protocol.
Question: What role is required to create a flow with a Service Catalog trigger in order to start a flow when a Service Catalog item is requested to automate the fulfillment process?
Answer: catalog_admin.
Question: How do you create a new role? What role is required?
Answer: Navigate to All > User Administration > Roles and create a new record.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/roles/task/t_CreateARole.html#t_CreateARole
Question: What role is required to personalize a form?
Answer: Either the itil, personalize_form, or admin role is required.
S
Save, Update, or Insert and Stay When Editing a Form
Question: What’s the difference between the Save button and Update button?
Answer: With Save, the user remains on the same record and with Update, the user returns to the previously viewed record.
Question: When updating a form, which two options will return you to the previously viewed page?
Answer: Click Submit or Update will save your changes and return to the previously viewed page.
Question: How do you save a form, and stay in the current form view?
Answer: Right-click the form header and select Save to save changes without leaving form view.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-forms/task/t_EditingInForms.html
Scheduled Jobs
Question: What are scheduled jobs?
Answer: Scheduled Jobs are automated pieces of work that can be performed at a specific time or on a recurring schedule.
Question: What types of tasks can you automate with Scheduled Jobs?
Answer: You can automate the following kinds of tasks:
• Automatically generate and distribute a report
• Automatically generate and schedule an entity of records, such as an incident, change item, configuration item, from a template
• Run scheduled jobs from scripts or business rules
• Scheduling at the end of the month
• Scheduling for weekdays
For developer training, see Scheduled Script Executions and Events Objectives on the ServiceNow Developer Site.
Scheduled Jobs Documentation: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/reference-pages/concept/c_ScheduledJobs.html
Schema Map
Question: What does Schema Map display?
Answer: The schema map displays the details of tables and their relationships in a visual manner, allowing administrators to view and easily access different parts of the database schema.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/table-administration/concept/c_SchemaMapForTables.html
Question: How do you generate a Schema Map?
Answer:
- Navigate to All > System Definition > Tables & Columns
- In the Table Names pane, select a table.
- Click Schema map. The schema map for the selected table opens in a separate tab or window.
Question: Does a Schema Map display Extended Tables, Extending Tables, and Reference Tables?
Answer: Yes
Question: How would you see the schema map for a configuration item?
Answer: Navigate to All > System Definition > Tables & Columns > Highlight the configuration item table, and click schema map
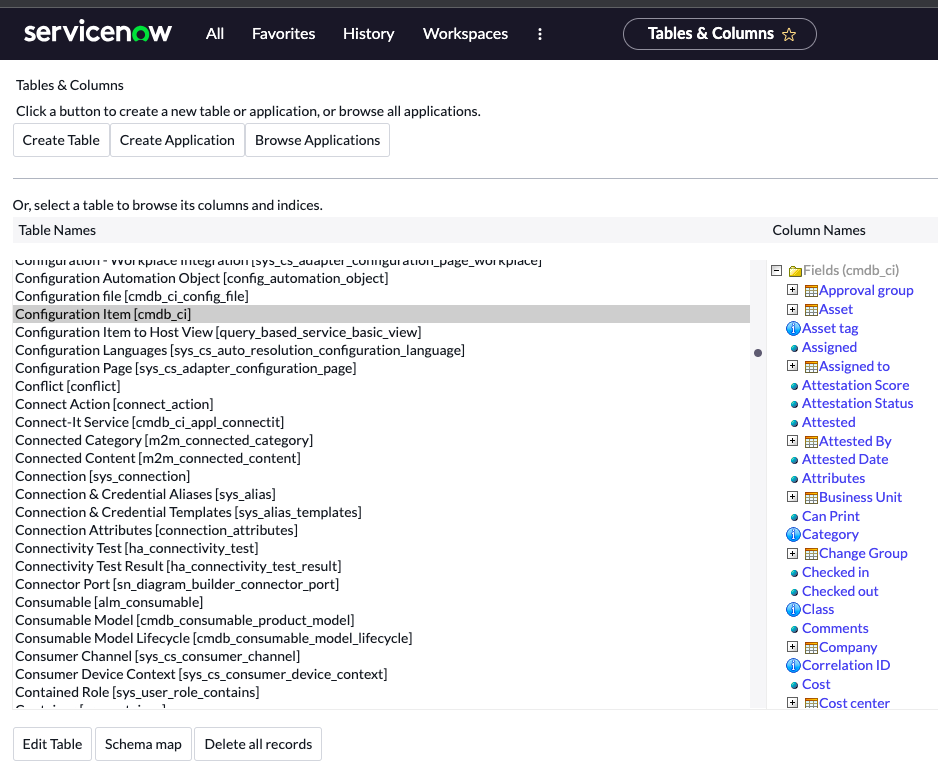
Scope
Question: What does application scoping do?
Answer: Application scoping protects applications by identifying and restricting access to application files and data.
Question: What is Global Scope?
Answer: Global Scope is a special application scope that identifies applications developed prior to application scoping or applications intended to be accessible to all other Global applications.
Scripts
Question: What are the available script types in ServiceNow?
Answer:
• Access Control
• Ajax Scripts
• Business Rules
• Service Catalog UI Policies
• Client Scripts
• Script Actions
• Script Includes
• Transform Maps
• UI Actions
• UI Context Menus
• UI Macros, UI Pages
• UI Policies
• UI Properties
• UI Scripts
• Validation Scripts
• Workflow Editor
Question: Where do client scripts execute?
Answer: On the browser and you may also run a client script when a database lookup is needed.
Question: What are the types of Client scripts supported?
Answer: onLoad(), onChange(), onSubmit(), and onCellEdit()
Script Includes
Question: What are Script Includes?
Answer: Script Includes are reusable server-side script logic that define a function or class.
Functions: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Functions
Class: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Classes
Classes are a template for creating objects. They encapsulate data with code to work on that data. Classes in JS are built on prototypes but also have some syntax and semantics that are unique to classes.
Functions are one of the fundamental building blocks in JavaScript. A function in JavaScript is similar to a procedure—a set of statements that performs a task or calculates a value, but for a procedure to qualify as a function, it should take some input and return an output where there is some obvious relationship between the input and the output. To use a function, you must define it somewhere in the scope from which you wish to call it.
Script Includes execute their script logic only when explicitly called by other scripts. There are different types of Script Includes:
• On demand/classless
• Extend an existing class
• Define a new class
Script includes are used to store JavaScript that runs on the server.
Create script includes to store JavaScript functions and classes for use by server scripts. Each script include defines either an object class or a function.
Consider using script includes instead of global business rules because script includes are only loaded on request.
Question: A Script Include is what?
Answer: Reusable code that runs server side.
Question: Do Script Includes run client-side or server-side?
Answer: Server-side.
Question: When do Script Includes execute their script logic?
Answer: Only when explicitly called by other scripts.
Question: What do Script Includes store?
Answer: They store JavaScript that runs on the server; JavaScript functions and classes that are used by server scripts. Each script include defines either an object class or a function.
Question: True or false? Script Includes are only invoked when called upon by the user.
Answer: True
Question: True or False? Script includes that have SNC in their names have a paired script which includes the same name but minus the SNC.
Answer: True
Question: How does Glide Ajax work with script includes?
Answer: The GlideAjax class allows the execution of server-side code from the client. GlideAjax calls pass parameters to the script includes, and, using naming conventions, allows the use of these parameters.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/utah-api-reference/page/script/ajax/topic/p_AJAX.html
Question: Why should you consider using script includes instead of global business rules?
Answer: Because script includes are only loaded on request.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/script/server-scripting/concept/c_ScriptIncludes.html
Scripting
Question: Which programming language is used for scripting in ServiceNow?
Answer: Javascript
*If you wish to learn Javascript in the context of ServiceNow, developer advocate Chuck Tomasi has great tutorials on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nK1aPdGyGak
Question: What are the available script types in ServiceNow?
Answer:
Ajax Scripts – Enables the client to get data from the server to dynamically incorporate into a page without reloading the whole page.
Business Rules
Question: Where do Client-side scripts execute?
Answer: Client-side scripts execute within a user’s browser and are used to manage forms and form fields.
Question: What types of Client Scripts are supported?
Answer: 1) onLoad() 2) onChange() 3) onSubmit() 4) onCellEdit()
Question: What are Client-side Scripts typically used for?
Answer: Client-side scripts are commonly used for:
• Placing the cursor in a form field on form load
• Generating alerts, confirmations, and messages
• Populating a form field in response to another field’s value
• Highlighting a form field
• Validating form data
• Modifying choice list options
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/script/client-scripts/concept/client-scripts.html
Search
Question: What is the default search engine in ServiceNow?
Answer: Zing is the default search engine used to search Now Platform record data.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/search-administration/concept/c_ZingTextSearch.html
Question: What are the options for list search?
Answer:
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/task/t_SearchAList.html
Question: What are the available search interfaces?
Answer:
1) Global Search – allow you to search multiple record types from a single search field.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/search-administration/concept/c_GlobalTextSearch.html
2) Search a List – The list title bar includes options for searching the list. Administrators can enable text searches for any list.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/task/t_SearchAList.html
3) Knowledge Base – Search for knowledge articles from the knowledge homepage using the search bar on the Knowledge Management v3 homepage.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/knowledge-management/reference/r_KnowledgeSearch.html
Documentation for Search interfaces:
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/search-administration/concept/c_IntroductionToSearching.html
Question: How would you search for all Incident records containing the string Down in the Short description field?
Answer: Enter *Down in the Search field.
https://developer.servicenow.com/dev.do#!/learn/courses/sandiego/app_store_learnv2_buildmyfirstapp_sandiego_build_my_first_application/app_store_learnv2_buildmyfirstapp_sandiego_servicenow_basics/app_store_learnv2_buildmyfirstapp_sandiego_exercise_navigation_lists_and_forms
Question: Are searches in lists case sensitive?
Answer: No.
Sections
Question: What are sections in Forms?
Answer: Sections are logical groupings of fields. By default, sections are rendered as tabs at the bottom of a form. The use of sections prevents users from having to scroll through long forms. Using a script, sections can be hidden when they are not needed.
Question: What do Sections help you do in Forms?
Answer: Sections help group related fields together.
Question: How do you create a Form Section?
Answer: Right-click the form header and select Configure > Form Layout
The rest of the instructions to create a Form Section can be found here:
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/form-administration/concept/configure-form-layout.html
Security
Question: Where can you access a playbook of instance security best practices?
Answer: In the Instance Security Best Practice Playbook:
Question: How do you limit file attachment size?
Answer: System > Security
Question: Is data encrypted in transit with ServiceNow?
Answer: Yes
Question: True or False? A user with the security_admin role can assign the security_admin role to other users?
Answer: True.
Question: How does Contextual Security Manager protect data?
Answer: By controlling read, write, create, and delete authorization.
Question: What settings can you make in the Contextual Security Manager?
Answer: Setting the maximum file attachment size, and attachment file types.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/utah-platform-security/page/administer/roles/reference/r_ContextualSecurity.html
Self-Service
Question: What does Self-service offer end users?
Answer: A clean, simple front end to their IT support organization.
Question: Which application is available to all users?
Answer: Self-Service
Question: Does the self-service application require a role?
Answer: No. Self-service is one of the few applications that do not require a role.
Question: Do Self-service users require a ServiceNow license in order to see a record’s form?
Answer: No. Most ServiceNow licensing is based on the number of fulfillers.
Question: What does a user have access to within Self-service?
Answer: The Self-Service application provides access to common actions, such as viewing your homepage, accessing the Service Catalog, viewing knowledge articles, working with incidents, and taking surveys.
Question: What does the self-service application give users access to by default?
Answer: By default, the self-service application provides access to common actions, such as viewing your homepage, accessing the Service Catalog, viewing knowledge articles, working with incidents, and taking surveys.
Service Catalog
Question: Which is true about Service Catalog Items in relation to the Service Catalog?
Answer: They are the building blocks of the Service Catalog. With the Service Catalog application, you can create service catalogs that provide your customers with self-service opportunities. You customize portals where your customers request catalog items like service and product offerings. You also standardize request fulfillment to ensure the accuracy and availability of the items in the catalogs.
Question: What is the main purpose of Service Catalog Workflow?
Answer: To drive complex fulfillment processes and send notifications to users or groups.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_ServiceCatalogWorkflowDefinition.html
Question: What are the main components of Service Catalog?
Answer:
1) Record Producers
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_RecordProducer.html
2) Request Items
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/planning-and-policy/concept/request-management-architecture.html
4) Order Guides
Question: How do you access the service catalog?
Answer: All > Self-service > service catalog
Once you click on Service Catalog, you’ll see options available to you:
Question: What do service catalog variables do?
Answer: Service catalog variables capture and pass on information about choices a customer makes when ordering a catalog item. Variables help define the structure of a catalog item form that is displayed to the customer.
Question: When you add a variable to a catalog item, what does the order field determine?
Answer: The order field establishes the display order of the Variables. Order that the variable is placed on the page for the catalog item. Variables are organized from top to bottom from least to greatest order value. For example, a variable with an order value of 1 is placed above other variables with higher-order values.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/task/t_CreateAVariableForACatalogItem.html
Question: What are the two Service Catalog workflows provided in the base system?
Answer: Two service catalog workflows are provided in the base system. Use the Graphical Workflow Editor to modify the default workflows or to create additional service catalog workflows. Service catalog workflows support domain separation.
1) Service Catalog Request – a simple workflow that fulfills a simple order.
2) Service Catalog Item Request – a more complex workflow that fulfills a more complex order.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_ServiceCatalogWorkflowDefinition.html
Question: In a Service Catalog Item, what controls the display sequence?
Answer: The order field in the variable form.
Question: What is the name of the namespace (a namespace is a set of signs (names) that are used to identify and refer to objects of various kinds) of the Service Catalog API?
Answer: sn_sc
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/integrate/inbound-rest/concept/c_ServiceCatalogAPI.html
Question: What is generated from the Service Catalog once a user places an order for an item or service?
Answer: A Request
Question: What is a REQ number in the Service Catalog?
Answer: An order number.
Question: What are the 3 types of numbers generated from orders??
Answer: REQ (Request number), RITM (Request Item), and SCTASK (Catalog Task Number).
Question: What do the services Create Incident, Password Reset, and Report Outage have in common when chosen by a user from the Service Catalog?
Answer: They direct the user to a Record Producer.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_RecordProducer.html
Question: What are the two options for defining the fulfillment process for a service catalog item?
Answer: Flow and Workflow.
Question: What is a Field?
Answer: Fields correspond to a column in a table. For example, the user’s email address or location.
Question: What is a Record?
Answer: Records correspond to a row in a table. For example caller + priority + state + category in the incident table.
Question: Service catalog workflow can be attached in 3 ways. What are they?
Answer:
- Manually on the catalog item form
- Automatically based on conditions
- Automatically if no other workflows are attached
Question: A Service Catalog may contain which of the following components?
Answer:
1) Record Producers
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/vancouver-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_ServiceCatalogOrderGuides.html
3) Standard Catalog Items
Question: Where do you go to add/modify a service catalog item?
Answer: Service Catalog > Maintain Item
Question: For Administrators creating new Service Catalog Items, what should they know about Service Catalog variables?
Answer: Service Catalog Variables are global by default.
Question: The display sequence is controlled in a Service Catalog item using what?
Answer: The order field in the variable form.
Question: When you add a variable to a catalog item, what does the order field determine?
Answer: The display order of the variables, listed by ascending order.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_ServiceCatalogVariables.html
Question: From the end user’s perspective, how are the products and services in the service catalog organized?
Answer: Categories and Subcategories
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_ServiceCatalogCategories.html
Question: A service catalog may include which components?
Answer: Record producers, order guides, and catalog items.
Question: The baseline Service Catalog homepage has links to which of the following components?
Answer: Record Producers, Order Guides, and Catalog Items.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_ServiceCatalogManagement.html
Question: What types of numbers are generated when an order is placed?
Answer: A Catalog Task Number (TASK), Request Number (REQ), and Requested Item (RITM).
Question: What aspects of the Service Catalog can Administrators manage?
Answer: All aspects:
• Catalogs, Categories
• Catalog Items
• Scripting Functions (like creating business rules)
They can also manage all aspects of the Service Catalog application, except scripting functions.
Question: What aspects of the Service Catalog can a Catalog Manager manage?
Answer: Edit and update the Service Catalog, including it’s categories and Catalog Items. They can also assign Catalog Editors and assign the Catalog to a different manager.
Question: What aspects of the Service Catalog can a Catalog Editor manage?
Answer: The same functions as the Catalog Manager: Edit and update the Service Catalog, including it’s categories and Catalog Items. However, they are not allowed to assign Catalog Editors and assign the Catalog to a different manager.
Question: How do you create a flow with a Service Catalog Trigger in order to start a Flow when a Service Catalog item is requested to automate the fulfillment process? What role is required to create a Trigger?
Answer: The flow_designer or admin role is required. See the following steps, starting with navigating to Service Catalog > Catalog Definition > Maintain Items.
The role required to create a trigger is catalog_admin.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/flow-designer/task/create-sc-flow.html
Question: What does Delegated Request Experience allow you to do?
Answer: Request a catalog item on behalf of another user or multiple users using the Requested For variable.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/delegated-request-exp.html
Question: How to you deactivate a product catalog item? What role is required?
Answer:
- Navigate to All > Product Catalog > Catalog Definition > Hardware and Software Items
- Perform one of these two steps: a) Deactivate from the list view or b) Deactivate from the record.
Question: What is a Service Catalog Variable Editor (VEditor)?
Answer: Variable editor displays variable values in fulfiller forms. A requester, while requesting the item, specifies these variable values in the catalog item questions.
The VEditor is applicable only for the requests created from catalog items.
In Now Platform, this editor is a formatter added on the requested item (RITM) form (Default View) and the catalog task form (Default View).
The VEditor is applicable only for RITMs and catalog tasks. It cannot be used for any other tables. To support catalog UI policies or catalog client scripts on the VEditor for the RITM and catalog task form, select the Applies on Requested Items and Applies on Catalog Tasks check boxes for the catalog UI policy or the catalog client script.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/service-catalog-variable-editor.html
Question: When can you not apply Delegated Request Experience?
Answer: When two-stop checkout is enabled.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/delegated-request-exp.html
Question: What are Execution Plans?
Answer: An Execution Plan describes how a catalog item is procured, configured, and installed.
Execution plans enable you to describe simple, linear processes. Each execution plan contains one or more tasks. For example, an organization could create an execution plan for delivering a corporate standard PC that contains these tasks:
- Procure the PC from a supplier.
- Configure the PC according to requester specifications.
- Deliver the PC to the requester.
An execution plan is not specific to any one catalog item. There could be many different models of PC that a user can order, all using the same execution plan. It is not necessary to create a new execution plan for each individual catalog item in a mature service catalog.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_ExecutionPlans.html
Question: How do you create an Execution Plan?
Answer:
Procedure:
- Navigate to All > Service Catalog > Catalog Administration > Execution Plans
- Click New
- Enter a Name and Short description for the execution plan.
- Specify delivery information in the Total delivery time and On Calendar fields.
- Click Submit.
Service Catalog Items
Question: What is true of Service Catalog Items?
Answer: They are the building blocks of the Service Catalog. The overall catalog is made up of a collection of discrete catalog items.
Question: What are the basic types of Service Catalog Items?
Answer: The basic Service Catalog item types include:
• Standard Catalog Items
• Record Producers: giving alternative ways of adding information such as incidents via the service catalog.
• Order guides: to group multiple catalog items in one request.
• Content Items: Catalog Items which provide information instead of goods or services. An example would be directing a user to a knowledge article.
Question: What is the most common order guide?
Answer: The new hire order guide.
Question: What does user criteria allow you to do?
Answer: User criteria enables you to allow access to users based on role, department, group, location, or company. Administrators can control access to pages, widgets, widget instances, announcements, and search sources in a portal by creating and applying user criteria. You can also restrict which catalog items users have access to with user criteria.
Service Catalog Variables and Variable Types
Question: What do you use Service Catalog Variables for?
Answer: To gather information from users ordering a catalog item, for example, to ask users which options they want for the item.
Question: Are Service Catalog Variables global by default?
Answer: Yes.
Question: Which three Variable Types can be added to a Service Catalog Item?
Answer: Multiple Choice, Select Box, and Checkbox.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/reference/r_VariableTypes.html
Question: How do you create a Service Catalog Variable?
Answer:
- Navigate to All > Service Catalog > Catalog Definitions > Maintain Items.
- Select the catalog item that you want to create a variable for.
- In the Variables related list, click New.
- Select the variable type. Only the applicable fields for the variable type are then displayed.
Question: The display sequence is controlled in a Service Catalog Item by what?
Answer: The order field in the Variable form.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/concept/c_DefineVariableSetLayout.html
Service Portal
Question: What does the Service Portal allow you to do?
Answer: Service Portal allows you to build a mobile-friendly self-service experience for your users. It interacts with parts of the Now Platform, so users can access specific platform features using Service Portal. It is an alternative to the Content Management System (CMS) based on more modern technologies.
Question: What technologies are incorporated into the Service Portal?
Answer:
1) Containers, rows, and columns
2) Widgets and widget instances
3) Bootstrap
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/build/service-portal/concept/c_ServicePortal.html
ServiceNow Platform
Question: What certifications does the ServiceNow platform have?
Answer:
• ISO 270001 – provides requirements for an information security management system. https://www.iso.org/isoiec-27001-information-security.html
• SSAE 18 – an auditing standard for service organizations.
• SOC 1 –
• SOC 2
To access the reports above, go to: https://support.servicenow.com/kb?id=kb_article_view&sysparm_article=KB0564067
Question: What does the ServiceNow multi-instance architecture look like?
Answer: Data, applications, and customizations reside in an instance. Each instance is isolated from every other instance, making maintenance easy to perform.
Question: What are the three ways to interact with the Now Platform?
Answer:
1) Next Experience Unified Navigation
2) ServiceNow Mobile App
3) Service Portal
Question: True or False? ServiceNow can be consumed as SaaS (Software-as-a-Service), and there is also a desktop version of the application for Windows and Mac.
Answer: False
Question: True or False? ServiceNow can be installed on premise (in the customer’s data center), or consumed as SaaS.
Answer: True.
ServiceNow Studio
Question: What is ServiceNow Studio?
Answer: ServiceNow Studio provides an Integrated Development Environment (IDE)-like interface for application developers to work on custom applications in one centralized location. It offers a simple way to create, review, and update application files from a tabbed environment. The system opens Studio whenever you edit a custom application.
Question: How do you navigate to ServiceNow Studio?
Answer: All > System Applications > Studio.
Question: What can you use to search for code inside and outside your ServiceNow application across all objects (Business Rule, Notification, any object).
Answer: Code Search
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/applications/concept/c_ServiceNowStudio.html
Service Portal
Question: What does the service portal allow you to do?
Answer: Service Portal allows you to build a mobile-friendly self-service experience for your users. It interacts with parts of the Now Platform, so users can access specific platform features using Service Portal. It is an alternative to the Content Management System (CMS) based on more modern technologies.
Question: How do you access the Service Portal homepage?
Answer: The Service Portal homepage can be accessed by navigating to https://.yourinstancename.com/sp In other words, append /sp after your instance URL. Or you can just go to All and type “service portal” and then click service portal home to see the out-of-the-box service portal. In the header, you’ll now see the options Request Something, Knowledge Base, and Get Help.

Question: What are users able to do in Service Portal?
Answer: Users can access a user-friendly self-service experience and specific features using widgets. Users are able to:
• Search for articles, catalog items, and records
• Submit requests
• Browse the corporate news feed
Question: How do you configure portal branding?
Answer: You use the Branding Editor to give your portal its own look and feel.
Question: How do you access the Branding Editor?
Answer: To access the Branding Editor, navigate to All > Service Portal > Service Portal Configuration, then click Branding Editor.
Sidebar
Question: What does the Sidebar allow agents to do?
Answer: Sidebar enables agents so they can collaborate with others when working on a Workspace task-based or interaction-based record.
SLAs
Question: What is an SLA?
Answer: A service level agreement (SLA) is a contract between a service provider and a customer, defining the types and standards of services to be offered. In the ServiceNow docs, an SLA is defined as “a record that specifies the time within which service must be provided.”
Question: What is the biggest benefit of utilizing SLAs?
Answer: They allow the Service Desk to have visibility into whether they are providing the appropriate level of service agreed upon with the business and run reports that show that incidents are closed or resolved according to the expectations set for customers.
Question: What are the four aspects of SLA?
Answer:
1) Task SLA
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/service-level-management/reference/r_TaskSLATable.html
2) SLA Workflow
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/service-level-management/concept/c_WorkflowsForSLA.html
3) SLA Automation
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/flow-designer/task/create-sla-task-flow.html
4) SLA Definition
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/service-level-management/task/t_CreateAnSLADefinition.html
Question: What are three types of SLAs?
Answer:
- SLA – Service Level Agreement
- OLA – Operating Level Agreement
- UC – Underpinning Contracts
Question: The SLA Type is defined in which field?
Answer: The Type field.
Question: Where do you see attached SLAs for each task?
Answer: Attached SLAs are accessible in a related list on the task’s form.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/service-level-management/reference/r_TaskSLATable.html
Question: Through Database Views in the base system, which of the following tables does the change_task_sla database view join?
Answer: change_task and task_sla.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/use/reporting/reference/r_DatabaseViewsInTheBaseSystem.html
Question: What do SLA Conditions determine?
Answer: SLA conditions determine when a task SLA record is attached, paused, resumed, reset, canceled, and completed.
Question: How many SLA Conditions you can set? What are they?
Answer: You can set up to six SLA conditions: start, cancel, pause, resume, stop, and reset.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/service-level-management/concept/c_SLAConditions.html
Question: What is an SLA Definition?
Answer: An SLA definition is used to create and progress SLAs, enabling you to use an SLA system for your organization’s tasks. An SLA definition is used to create and progress SLAs, enabling you to use an SLA system for your organization’s tasks. An SLA definition record defines the timings, conditions, workflows, and other information required to create and progress task SLAs.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/service-level-management/concept/c_SLADefinitions.html
Question: In SLA Definition, what are the main conditions that will trigger an SLA?
Answer: Start condition, Pause condition, and Stop condition
Question: Which table defines what conditions trigger an SLA?
Answer: contract_sla
Question: Can you create a Workflow from an SLA Definition?
Answer: Yes, you can automate a multi-step process by creating a workflow from an SLA definition.
Question: How do you create a Workflow from an SLA Definition?
Answer:
- Open a list of SLA definitions. For example Facilities > SLA Definitions or Service Level Management > SLA Definitions
- Follow the rest of these instructions:
Question: True or False? In SLA, Retroactive Start allows setting the start time to a time from an earlier event?
Answer: True.
Question: What is an example of when you would use Retroactive Start?
Answer: An incident is raised with a priority of 3 – Moderate and the priority changes to 1 – Critical after 3 hours. A priority 1 SLA is attached to the incident at that time. You can use retroactive start to ensure this SLA timing is adjusted retroactively to count from when the incident was first created, rather than from when the incident’s priority changed. This reflects the actual time the user contacted you.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/service-level-management/task/t_UseSLARetroactiveStartAndPause.html
Question: What is the sequence of conditions in an SLA Definition?
Answer: Start, Pause, and Stop.
Question: What does the Start condition do?
Answer: It triggers the SLA.
Question: What does the Pause condition do?
Answer: Enables you to define the conditions under which the SLA will suspend increasing elapsed time.
Question: How do you create a new SLA Definition?
Answer: All Menu > Service Level Management > SLA Definitions
Question: Which base table stores Task SLA records for the SLAs attached to particular tasks?
Answer: The task_sla table.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/service-level-management/reference/r_TaskSLATable.html
Question: Which dashboard lets you see incidents that are overdue according to an SLA, divided by the New, In Progress, and On Hold states?
Answer: The Overdue by State dashboard.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/use/dashboards/application-content-packs/overdue-state-dashboard.html
Question: What does SLM stand for?
Answer: Service Level Management.
Stats Module
Question: Where do you check which release is running on instance?
Answer: In the Stats Module.
Question: How do you access the Stats module?
Answer: All > System Diagnostics > Stats
Question: What is the Stats module used for?
Answer: It is used to aid in performance evaluation, and provides statistics for system activities that affect performance such as the execution of queries, scripts, and transactions. The module is also commonly used to lookup which version, patch, and hotfix your instance is running.
Question: How do you check which release and patch version your ServiceNow version your instance is at?
Answer: All > System Diagnostics > Stats > Stats.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/platform-performance/concept/c_StatsToolsDiagnosticsPlugin.html
States
Question: What are the default states during an Incident lifecycle?
Answer:
- In Progress
- On Hold
- Resolved
- Closed
- Canceled
System Dictionary
Question: What information does the System Dictionary contain?
Answer: The information for each table and column.
The system dictionary is a table, called Dictionary Entry [sys_dictionary], that contains details for each table and the definition for every column on each table in an instance.
Each row in the system dictionary represents either a table or a column in one of the tables. The system dictionary provides options for administrators to modify tables and fields, which in turn define lists and forms.
Use caution when changing system dictionary records because changes can have a high impact on functionality. In particular, changes to dictionary entries for system tables, which are tables that begin with sys_, can create system-wide issues such as the inability to use update sets. Dictionary changes are difficult to reverse. Also, dictionary changes automatically apply to all extended tables unless a dictionary override is defined. Be sure that changes are well-tested before applying them to a production instance.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/data-dictionary-tables/concept/c_SystemDictionary.html
Question: How do you modify Dictionary Entries?
Answer: You can modify dictionary entries by configuring a field on a form or from the Dictionary module.
- Do one of the following steps: Navigate to a field on a form, right-click the field, and select Configure Dictionary or Show The system dictionary entry for the field opens. Navigate to System Definition > Dictionary, and click an entry for a field or table. Entries for tables have Type set to Collection.
- Update the dictionary entry fields.
- Click Update
System Logs
Question: Where do you go to use logs for application activity history, troubleshooting and debugging transactions, and events that have taken place within the instance?
Answer: System Logs.
Question: What logs are available from the System Logs module?
Answer: Transactions, Email and Push, Events, Import, Table Changes (Changes made to all tables in the system), Outbound web services logging, Signature Images, and System.
System Properties
Question: What do system properties do?
Answer: System properties are like key:value pairs. System properties store configuration information that rarely or never changes. Each time you change or add a system property, the system flushes the cache to keep all nodes in the cluster in sync. This cache flush has a very high performance cost for one to 10 minutes, which can potentially cause an outage if done excessively. To prevent such outages, don’t use a system property to store configuration information that changes more than once or twice a month. Instead, use a custom table to store regularly changing configuration information.
Question: Where are system properties maintained?
Answer: System properties are maintained in sys_properties table.
Question: What are some common system properties?
Answer: List v3, UI properties, email properties, system properties, and global text search properties
Question: How can you see the list view of all system properties?
Answer: Type sys_properties.list Click into one of the properties to see the form view of that property.
T
Tables and Fields
Question: What is a table?
Answer: A collection of records in the database into which information can be entered.
Question: Which type of tables can be extended by other tables, but do not extend another table themselves?
Answer: Base Tables.
Question: What is one reason administrators and application developers extend tables?
Answer: In order to share information between related records.
Question: True or False? Base system tables can be deleted?
Answer: False
Question: Fill in the blanks: A table that extends another table is called a ______ , and the table it extends is the _________.
Answer: Child Class and Parent Class.
Question: Can you delete a custom table that extends from another table?
Answer: No.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/table-administration/concept/c_DeleteATable.html
Question: In what order are Table Access Control rules applied ?
Answer: Table name > Parent table name > Any table name (*wildcard)
Question: Which is the parent table for incident, problem, and change, all of which are Base Tables.
Answer: task.
Question: Are tasks created directly on the task table?
Answer: No, tasks are created on task child tables.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/task-table/concept/c_TaskTable.html
Question: What is the System Dictionary, and what does it contain?
Answer: The system dictionary is a table, called Dictionary Entry [sys_dictionary], that contains details for each table and the definition for every column on each table in an instance.
Each row in the system dictionary represents either a table or a column in one of the tables. The system dictionary provides options for administrators to modify tables and fields, which in turn define lists and forms.
Use caution when changing system dictionary records because changes can have a high impact on functionality. In particular, changes to dictionary entries for system tables, which are tables that begin with sys_, can create system-wide issues such as the inability to use update sets. Dictionary changes are difficult to reverse. Also, dictionary changes automatically apply to all extended tables unless a dictionary override is defined. Be sure that changes are well-tested before applying them to a production instance.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/data-dictionary-tables/concept/c_SystemDictionary.html
Question: What is the master table that contains a record for each table in the database?
Answer: sys_db_object
Question: Which table tracks changes to Update Sets?
Answer: The sys_update_set table.
Question: In regards to table relationships, what is the most common relationship?
Answer: One to many.
Question: What is one example of a many-to-many table relationship?
Answer: Each user can belong to multiple groups. Each group can have many users.
Question: Which table contains user data?
Answer: sys_user
Question: What is the name of the visual diagram that shows table relationships?
Answer: The schema map.
Question: What is the table name for the user table?
Answer: sys_user
Question: What are two methods of accessing the sys_user table?
Answer: Either type sys_user.LIST or navigate to All > User Administration > Users.
1) Type sys_user.LIST in the Application Navigator to see a list of users.
2) Or navigate to All > User Administration > Users.
Question: Which table holds the maximum number of activities to display on the History tab?
Answer: sys_properties
Question: Should you modify or delete a sys_id?
Answer: No Modifying or deleting a sys_id results in bad or lost data.
Question: What is the DB name for a custom table?
Answer: u_tbl
Question: What would a custom table that extends the incident table possibly be named?
Answer: u_incident
Question: In which table are Business Rules stored?
Answer: sys_script
Question: Which table stores information about CI relationships?
Answer: cmdb_rel_ci
Question: In what order are table access controls processed?
Answer: table name, then parent table name, then any table name (wildcard)
Question: What are Database Views?
Answer: A database view defines table joins for reporting purposes. For example, a database view can join the Incident table to the Metric Definition and Metric Instance tables. This view can be used to report on incident metrics and may include fields from any of these three tables. Several useful database views are installed with the Database View plugin and the Database Views for Service Management plugin. These database views cover most metric reporting needs and greatly reduce the need to define new ones. Any user who can create a report can use database views as the report source, but ACLs on the underlying tables are honored.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/use/reporting/concept/c_DatabaseViews.html
Question: How are tables related to each other?
Answer: There are four ways tables can be related to each other:
1) Extensions: A table can extend another table. The table doing the extending (child class) includes all of the fields of the other table (parent class) and adds its own fields. For instance, the Incident [incident] table has all of the Task [task] table fields (because an incident is a special form of task) and has its own incident-specific tasks.
2) One-to-Many: Within a table, a field can hold a reference to a record on another table.
3) Many-to-Many: Two tables can have a bi-directional relationship, so that the related records are visible from both tables in a related list.
4) Database Views: Two tables can be joined virtually with Database Views to enable reporting on data that might be stored over more than one table.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/service-level-management/reference/r_TaskSLATable.html
Question: How can you see a list of tables extended from another table, for example, the task table?
Answer: All > Tables > Search for the table name in the upper left
After clicking Tables, search for the table name, task in this case.
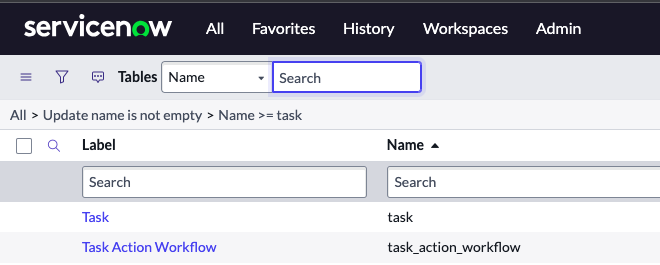
Question: What is a Schema Map?
Answer: The schema map displays the details of tables and their relationships in a visual manner, allowing administrators to view and easily access different parts of the database schema.
The schema map can also be printed directly from a browser.
Question: What do incident, problem, and change all have in common?
Answer: They all save to the task table.
Question: How do you create a many-to-many relationship?
Answer:
- In the navigation filter, enter sys_m2m.list
- Click New
- In the From table field, specify a parent table.
- In the To table field, specify a child table.
The Many-to-Many form automatically populates the other fields with suggested values - (Optional) Edit other field values, if appropriate. Many-to-Many table names cannot exceed 30 characters.
Question: From where can you view and manipulate tables?
Answer:
- In the record list
- From the Form
- In Tables and Columns
Question: How do you access the Tables & Columns Module?
Answer: System Definition > Tables & Columns
Question: What can you customize in ServiceNow?
Answer: Forms, tables, and fields.
Question: What are two things are created by default when you create a new table in ServiceNow?
Answer:
- An Application Menu with the same name as the table Label
- A Module with the plural of the table Label
Question: Which modules can you use to create a new table? Provide 2 Answers:
Answer: - Tables
- Tables & Columns
Question: How are Tables accessed?
Answer: Tables can be accessed using the following modules within the System Definition application:
Dictionary – defines every table and field in the system. Table records are identified as a Collection type.
Tables – contains a record for each table in the database. Custom tables can be created when the New button is created.
Tables & Columns – lists existing tables in the database. Selecting a table name displays its contents.
Question: What does the System Dictionary contain?
Answer: The System Dictionary contains the definition for each and every table and field in the database. Navigate to All > System Definition > Dictionary to access the system dictionary to modify table and field.
Question: What is a table?
Answer: A collection of records in the database. Each record corresponds to a row in a table, and each field on a record corresponds to a column on that table.
Question: Which module is used to view field settings for a table?
Answer: Tables & Columns.
Question: How is the module Tables & Columns accessed?
Answer: Navigate to All > System Definition > Tables > Tables & Columns
Question: Fill in the blanks. A _ is a column and a __ is a row.
Answer: A Field is a column, and a Record is a row.
Question: What is stored in a table?
Answer: Data.
Question: Can out of the box tables like Incident or change tables be deleted?
Answer: No.
Question: What are some examples of out-of-the-box tables?
Answer: incident, change_request, and cmdb_ci
Question: What role do you need to create a new table?
Answer: The admin role.
Question: In a table, what types of fields does ServiceNow support?
Answer: HTML, String, and Script.
Question: How do you create a new table?
Answer: From All > System Definition > Tables > Click New.
Question: Are all custom tables in the global namespace prefixed with a u_?
Answer: Yes.
Question: Can any table be deleted?
Answer: No, only tables beginning with “u_” can be permanently deleted.
Question: How do you delete a table?
Answer: From the All > System Administration > Tables > Tables & Columns.
Question: What should you delete before you delete a table?
Answer: All records in that table.
Question: What are some examples of related records to a table?
Answer: Reports, forms, form sections, ACLs, and reference fields.
Question: What is a many-to-many relationship?
Answer: Many-to-many relationships allow a list to point to a list of entries, rather than to single field.
Question: What is an example of a one-to-many table relationship?
Answer: Where the incident assigned to field in the incident table references the user table (sys_user).
Question: What are the three types of one-to-many relationship fields?
Answer: Reference Field, Glide List, and Document ID Field.
Question: What do you create Document ID fields for?
Answer: You create document ID fields to reference any record on any table.
Question: How to you create a Document ID field? (personalize_dictionary role required)
Answer: Procedure
- Navigate to the form view for the table.
- Right-click the header and select Configure > Form Layout
- Follow the rest of these instructions:
Question: What is Database View?
Answer: A Database View defines table joins for reporting purposes.
For example, a Database View can join the Incident table to the Metric Definition and Metric Instance tables. This view can be used to report on incident metrics and may include fields from any of these three tables.
Several useful database views are installed with the Database View plugin and the Database Views for Service Management plugin. These database views cover most metric reporting needs and greatly reduce the need to define new ones.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/use/reporting/concept/c_DatabaseViews.html
Question: What are Data Dictionary tables?
Answer: The system defines data dictionary, data modeling, and entity relationship information in multiple tables.
• Tables [sys_db_object]: Contains a record for each table.
• Dictionary Entries [sys_dictionary]: Contains additional details for each table and the definition for every column on each table. Each row represents either a column on a table or a table.
• Field Labels [sys_documentation]: Contains the human-readable labels and language information.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/managing-data/concept/c_DataDictionaryTables.html
Question: What is the difference between a core table and a base table?
Answer: A Core Table is any table that exists by default in the baseline instance. The way to think of Base Tables is to think of newly created tables that have the u_ prefix. With Base Tables the table is extended but itself is not extending any other table. Core Tables are the tables that exists in the base system, coming out of the box when you first are handed your instance login and password.
There’s a great Community article on the subject here:
Tables and Fields
Question: What are tags?
Answer:
Tags are text labels that you can associate with items like records and pages. Tags enable you to group and organize the items. Tags can be visible to any user (global), visible only to specific groups or users (shared), or visible to a single user (private).
Tags are stored in the Tag [label] table. To view tags in a list, navigate to System Definition > Tags or Self-Service > My Tags.
Table Extension and Classes
Question: What do Table Extensions allow you to do?
Answer: Enable one or more child tables to share fields and records with a parent table. Administrators and application developers can only extend tables during table creation.
Administrators and application developers typically extend tables to create a set of related records that share information. For example, in the base system, the Task and the Configuration Item tables have multiple extensions.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/table-administration/concept/table-extension-and-classes.html
Question: Which type of Tables may be extended by other Tables, but don’t extend another table?
Answer: Base Tables
Question: What is the relationship between the change table and the task table?
Answer: The change table extends the task table.
Tagging a Record
Question: How do you add a tag to a record?
Answer: Open the record, and click the More icon (…) in the upper right.
Question: How are two ways to edit tags after they’ve been created?
Answer:
- Navigate to a list that contains records you have previously tagged.
- From the form view, you can edit tags that you created.
Task
Question: What is a task?
Answer: A task is any record that can be assigned or completed by a user in ServiceNow. Users create tasks and are notified as the task moves along a workflow. Tasks can be assigned to specific users or user groups.
Question: What is created, has work performed on it, and then moves to an ultimate state of closed?
Answer: A task.
Question: Are tasks created directly on the task table?
Answer: No, tasks are not created directly on the task table. Instead, tasks are created on task child tables.
Question: What are common tables that extend the task table?
Answer: Incident, problem, and change request.
Question: What are four ways you can collaborate on tasks with other members of your team?
Answer: You collaborate on tasks with these four methods:
1) User Presence
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/navigation/concept/c_UserPresence.html
2) Activity Stream
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-customer-service-management/page/product/customer-service-management/concept/migration-activity-stream.html
4) Connect Chat
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/use/collaboration/concept/c_Collaboration.html
Question: There are four steps to assign tasks. What are they?
Answer:
- Add users to groups (like add a Helpdesk Analyst to the Service Desk Group)
- Apply roles to groups
- Assign tasks to groups
- Assign tasks to users
Question: What are Assignment Rules?
Answer: Assignment rules are used to automatically set a value in the Assigned to and/or Assignment group fields of a task record.
Question: Where do you view Assignment Rules?
Answer: By navigating to the All > System Policy > Rules > Assignment module.
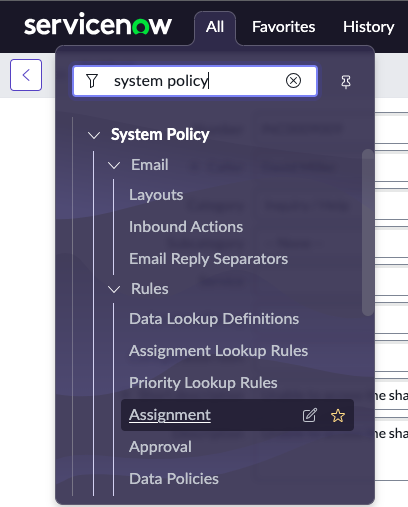
Question: What are the steps to create a new Assignment Rule?
Answer: After navigating to All > System Policy > Rules > Assignment module, click New in the upper right.
On the Assignment Rules form, type Hardware Issues (or whatever the Assignment rule is) in the Name field.
Set Conditions to Category is Hardware (or whatever the category is, like Database, etc.) This means when a Category of Hardware is selected on an incident, apply this assignment rule.
Select the Assign To tab to identify the Assignment group and User. You can do a lookup by typing the group name, and clicking the magnifying glass for a lookup.
Transform Maps
Question: What are Transform Maps?
Answer: A transform map is a set of field maps that determine the relationships between fields in an import set and fields in an existing ServiceNow table, such as Incident [incident] or User [sys_user].
Question: What provides a guide for moving data from import sets?
Answer: Transform Map
Question: Which columns does the Transform Map match?
Answer: A Transform Map matches the columns from the staging table to the columns in the target table. Every import operation requires at least one transform.
Question: Once defined, can a Transform Map be reused?
Answer: Yes
Question: Can the same Transform Map be reused multiple times on the same Import Set?
Answer: Yes
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/script/server-scripting/concept/c_CreatingNewTransformMaps.html
Question: Which application do you use to load data from a data source?
Answer: System Import
Trigger
Question: What initiates a Flow?
Answer: A Trigger.
Question: What are three Flow Trigger Types?
Answer: Created or Updated
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/flow-designer/reference/flow-triggers.html
Question: In the process of creating a new Flow, where is a Trigger added?
Answer: Step five in the process outlined here:
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/flow-designer/task/create-flow.html
UI User Interface
Question: What are the main UI components in ServiceNow?
Answer: The Content Frame, Application Navigator (or All Menu), and the Header.
UI Actions
Question: What do UI Actions include?
Answer:
- Form buttons
- Form context menu items (right-click the header)
- Form links (Related Links in a form)
- List buttons
- List context menu items (right-click a record)
- List choices (at the bottom of a list)
- List links (related links at the bottom of a list)
Question: Do UI Actions run client-side or server-side?
Answer: Both client-side and server-side. They typically run server-side, but optionally you can choose to run them client-side as well.
Question: Buttons, Form Links, and List Context Menu Items are examples of what type of functionality?
Answer: UI Actions.
Question: How do you create a UI Action?
Answer: Open the appropriate form, and go to the Context Menu > Configure > UI Actions, or right click on the header, and then Configure > UI Actions.
Question: Can you leverage Javascript with UI Actions?
Answer: Yes.
Question: What are some common use cases for UI Actions?
Answer:
- Integration with another SaaS platform (i.e. update Salesforce).
- Create a Problem.
- Create a button on the incident form to copy incident details, and create a child incident underneath it.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-it-service-management/page/product/change-management/task/t_CreateNewUIAction.html
UI Basic Configuration
Question: What are some of the most common things you configure in Basic Configuration?
Answer: The banner image, System date format, and Browser tab title.
Question: Where do you navigate to to make configuration changes?
Answer: All > System Properties > Basic Configuration
UI Pages
Question: What are UI Pages used for?
Answer: UI pages can be used to create and display forms, dialogs, lists, and other UI components. They are used as Widgets on a dashboard.
Question: How do you find UI Pages?
Answer: Navigate to All > System UI > UI Pages.
UI Policies
Question: What are UI Policies?
Answer: UI policies dynamically change the behavior of information on a form and control custom process flows for tasks. UI policies dynamically change the behavior of information on a form and control custom process flows for tasks.
Question: What is one benefit of using UI Policies over client scripts?
Answer: You get faster load times with UI Policies.
Question: What are some common things achieved with UI Policies?
Answer: You can use UI policies to make the number field on a form read-only, make the short description field mandatory, and hide other fields. Basic UI policies do not require any scripting, however for more advanced actions, use the Run scripts option. Another example of a UI Policy would be when you change the state to Resolved, a close code is required. If no close code is provided, an alert box would pop up saying you need to add a close code.
Question: What is the role required to create a UI Policy?
Answer: ui_policy_admin
Question: For UI policy to be applied on every view, which among the following should be checked?
Answer: Global.
Question: Do you usually use scripting when creating a UI Policy?
Answer: No, scripting is not usually required.
Question: How do you view existing UI Policies?
Answer: When in the form, Click the Context Menu > Configure > UI Policies
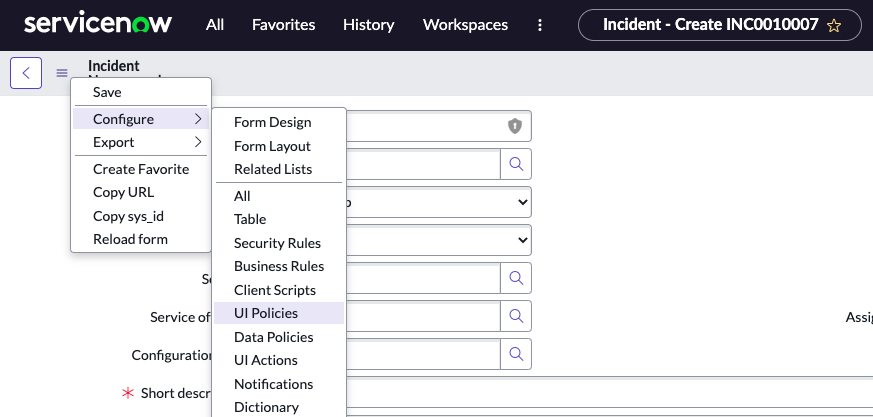
You will now see a list of UI Policies
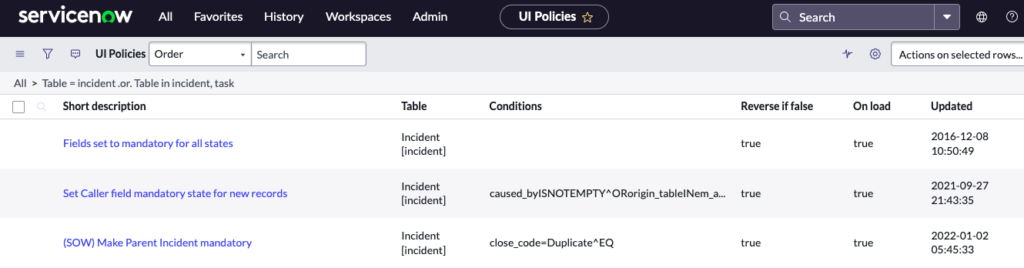
Question: How do you create a new UI Policy?
Answer: Navigate to All > System UI > UI Policies > Click New
Question: How do you create a new UI Policy when in a form?
Answer: Click the Context Menu at the top left of the form > Configure > UI Policies
UI Policy Actions
Question: What attributes of a field can a UI Policy action change on a form? Give three answers.
Answer:
1) Setting a field as visible or hidden
2) Setting a field as read-only, which prevents a user from updating its value.
3) Setting a field as mandatory.
UI User Interface and Unified Navigation
Question: What is Next Experience Unified Navigation?
Answer: Next Experience Unified Navigation is the primary way to interact with the applications and information in a ServiceNow instance. Notable Next Experience features include landing pages and navigation menus designed with tabs for all applications/modules, favorites, history, and workspaces. The Contextual app pill provides the context for where you are in the system.
Question: What are the four (now three in UI16) main UI16 components?
Answer:
1) Banner Frame – Runs across the top of every page and contains a logo and the following information, controls, and tools.
2) Application Navigator – Also called the left-navigation bar. Provides links to all applications and modules.
3) Content Frame – Displays information such as lists, forms, dashboards, and wizards.
4) The Edge – The Edge is removed in UI16. The collapsed view of the UI16 application navigator is similar to the Edge.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/administer/navigation-and-ui/concept/c_UI16.html
Question: What are the four distinct zones in Unified Navigation?
Answer: Logo, Navigation tabs (All, Favorites, History, and Workspaces), Contextual App Pill, and Utilities
Question: What do you use to change header bar color across an instance globally?
Answer: CSS Properties.
Question: What are Bookmarks? What replaced Bookmarks in UI16?
Answer: A bookmark is a link to information in the ServiceNow system, such as a record or a module, that is stored on the Edge. Favorites replaced Bookmarks in UI16.
Question: How do you customize the UI for yourself?
Answer: You can define system settings to customize the UI for yourself. The gear icon, located within the banner frame, displays the system settings pop-up window.
Question: What does not appear in the history section of the Application Navigator (now All Menu)?
Answer: UI Pages and other non-standard interfaces.
Question: How is History organized?
Answer: Chronologically.
Question: From the User Menu, which actions can a user select?
Answer:
1) Log out of ServiceNow
2) Elevate Roles
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/security/task/t_ElevateToAPrivilegedRole.html
3) Impersonate a User
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/users-and-groups/concept/c_ImpersonateAUser.html
3) Access System Settings for the User Interface via clicking Preferences (the Gear Icon). When you make changes to System Settings, it only affects the logged in user, not all users, and changes only take effect to the instance currently logged into.
https://docs.servicenow.com/en-US/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/administer/navigation-and-ui/reference/r_UI16BannerFrame.html
Question: Which term refers to application menus and modules which you may want to access quickly and often?
Answer: Favorite
Question: What are the main UI components of the ServiceNow platform?
Answer: The Application Navigator (or All menu now in Next Experience UI), the Content Frame, and the Banner Frame.
Question: What does clicking the Now logo do?
Answer: Takes you back to your home landing page.
Question: What does clicking the profile icon give you access to?
Answer:
- Customize your preferences
- Impersonate user
- Elevate role
- Access a printer friendly version
- Logout
Question: What appears in the history section of the Application Navigator (now All menu)?
Answer: Records, Lists, and Forms.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/rome-platform-user-interface/page/use/navigation/concept/c_ApplicationNavigation.html
Question: Which term refers to application menus and modules which you may want to access quickly and often?
Answer: Favorite
Question: Question: How do you access the additional actions menu?
Answer: It’s the hamburger icon in the upper left.
Question: What will appending $navpage.do to your instance name URL do?
Answer: Return you to the standard web browser interface.
Question: What will appending $tablet.do to your instance name URL do?
Answer: It will simulate a tablet environment on your PC browser.
Question: What will appending $m.do to your instance name URL do?
Answer: It will simulate a mobile environment on your desktop / laptop browser.
Unified Navigation Header
Question: What elements does the Unified Navigation Header include?
Answer: All, Favorites, History, and Workspaces.
Uninstall an Application
Question: How do you uninstall an application?
Answer: Navigate to System Applications > All Available Applications > All.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/applications/task/t_UninstallApplications.html
Universal Task Templates
Question: What are Task Templates used for?
Answer: Task Templates are used to auto-populate a Universal Task form. Using a task template enables agents to create tasks faster.
Question: What are Universal Task Templates used for?
Answer: Universal Task Templates help agents to create Universal Task records by auto-populating fields in a template.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-employee-service-management/page/product/universal-task/concept/ut-task-template-landing.html
Update Sets
Question: What are Update Sets?
Answer:
An update set is a group of configuration changes that can be moved from one instance to another. This feature allows administrators to group a series of changes into a named set and then move them as a unit to other systems for testing or deployment.
An update set is an XML file that contains:
• A set of record details that uniquely identify the update set.
• A list of configuration changes.
• A state that determines whether another instance can retrieve and apply configuration changes.
Update sets track changes to applications and system platform features. This allows developers to create new functionality on a non-production instance and promote the changes to another instance.
Question: What is the main purpose of an Update Set?
Answer: To create a standard process for moving customizations from instance to instance.
Question: In regards to Update Sets, What does ServiceNow recommend against?
Answer: Avoid using the Default Update Set as an Update Set when moving customizations from instance to instance.
Question: By default in ServiceNow, what customizations are added to update sets?
Answer: Changes made to a form.
Question: How are Workflows moved between instances?
Answer: With Update Sets.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/workflow-administration/concept/c_WorkflowMovementWithUpdateSets.html
Question: What customizations are tracked by Update Sets and under what conditions?
Answer: Customizations that have been made to application tables, fields, and records.
Update sets track customizations under these conditions:
• Where the table has an update_synch dictionary attribute.
• Where there is a special handler to track changes to multiple tables.
• Where the administrator has not excluded a field from updates.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/system-update-sets/reference/customizations-tracked-update-sets.html
Question: How do you report on customizations and configuration changes?
Answer:
- Navigate to All > Reports > View / Run and locate the Customer Update section.
- Run any of the available reports or create a new report. The following reports are available:
Application Changes (Incident): Displays all changes made to the Incident table. Select a different table and run the report again to view all changes to another application.
My Changes: Displays all changes created or updated by the current user, grouped by table name.
Question: Which records are captured in Update Sets?
Answer: UI Policies and UI Actions, Script Includes, and System Properties.
Question: What changes are captured in an update set?
Answer: Changes made to tables, forms, schedules, and client scripts.
Question: Can you back out an update set?
Answer: Yes.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/system-update-sets/task/t_BackOutUpdateSet.html
Question: Can you set the default Update Set to Completed?
Answer: Yes, and the system creates a new update set for the global application scope in the process.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/system-update-sets/reference/default-update-sets.html
Question: Can you merge Update Sets?
Answer: Yes.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/system-update-sets/task/t_MergeUpdateSets.html
Question: Which table tracks changes to Update Sets?
Answer: The sys_update_set table.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/system-update-sets/concept/system-update-sets.html
Question: Is workflow which has not been published yet captured in an Update Set?
Answer: No.
Question: What are the steps to commit an Update Set?
Answer: Mark the Update Set Complete > Retrieve > Commit
To Mark Complete: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/build/system-update-sets/task/t_CompleteUpdateSets.html
Upgrades and Upgrade Wizard
Question: What is Upgrade Wizard?
Answer: A step-by-step guide to help customers reduce the time to upgrade through easy-to-follow navigation.
Question: How do you access the Upgrade Wizard?
Answer: Within the instance dashboard page, click on Upgrade Now at the top of the page. Documentation is on the Support page: https://support.servicenow.com/kb?id=kb_article_view&sysparm_article=KB0541128
Question: If you need to see upgrade history, where do you do so?
Answer: System Diagnostics > Upgrade History
Question: Where do you go to see the current version?
Answer: stats.do
User Criteria
Question: How do you control access at the knowledge base level?
Answer: Through User Criteria. You specify user criteria for a knowledge base to control which users are granted access to read and contribute knowledge articles to that knowledge base.
Question: How do you create a User Criteria record in order to control access?
Answer:
Navigate to All > Knowledge > Administration > Knowledge Bases, Click the link to the knowledge base you manage, add user criteria to the knowledge base, and then depending on the user criteria you want to set, select one or more of the relevant related lists.
Question: How do you create user criteria for controlling access to knowledge bases and articles?
Answer:
1) Navigate to All > Knowledge > Administration > User Criteria
2) Click New
3) On the User Criteria form, fill in the fields
https://support.servicenow.com/kb?id=kb_article_view&sysparm_article=KB0550924
Question: Besides Knowledge bases, where would User Criteria typically be applied?
Answer: In the Service Catalog.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/product/service-catalog-management/task/t_CreateAUserCriteriaRecord.html
Question: Which roles can maintain user criteria?
Answer: user_criteria_admin
Question: Where would you see user criteria for a knowledge category?
Answer: Go to knowledge > administration > knowledge bases > open the knowledge category (I.T. in this case). Under related links, click Can Read, Can Contribute, Cannot Read, or Cannot Contribute to see privileges by group.
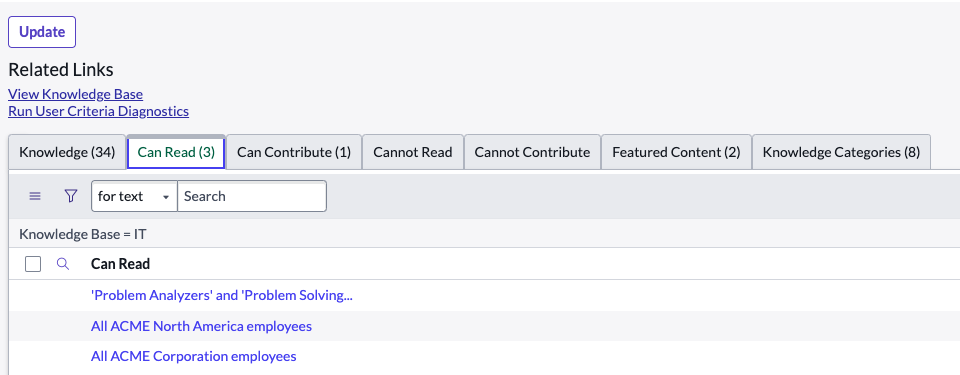
Users
Question: What does a user represent in ServiceNow?
Answer: An account and a single record in the sys_user table.
Question: How can you see all users in the sys_user table?
Answer: Type sys_user.list
User Impersonation
Question: What is the main purpose of impersonating a user?
Answer: For testing and visibility.
Question: How do you impersonate a user?
Answer: From the user menu, select the Impersonate a User option.
Administrators can impersonate other authenticated users for testing purposes and view impersonation logs. When impersonating another user, the administrator has access to exactly what that user can access in the system, including the same menus and modules. The instance records anything the administrator does while impersonating another user as having been done by that user.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/users-and-groups/concept/c_ImpersonateAUser.html
Question: Does the impersonator role allow you to impersonate admin or security_admin roles?
Answer: No.
User Menu
Question: From the User Menu, which actions can a user select?
Answer:
1) Log out of ServiceNow
2) Elevate Roles
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/security/task/t_ElevateToAPrivilegedRole.html
3) Impersonate a User
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-administration/page/administer/users-and-groups/concept/c_ImpersonateAUser.html
User Table
Question: What is the User Table named?
Answer: sys_user
V
Variables and Variable Sets
Question: What are Variables?
Answer: Variables provide questions that help the requester specify what item, option, or service to order.
Question: What are Variable Sets?
Answer: A collection of variables that can be shared across multiple Catalog Items and Order Guides. Variable Sets are useful when asking the same questions across different Catalog Items like: requested for, needed by, etc.
Question: How do you access Variable Sets?
Answer: All > Service Catalog > Catalog Variables > Variable Sets
If you open the Standard Employee Questions variable set, for example, you see the variables requested_for, and needed_by
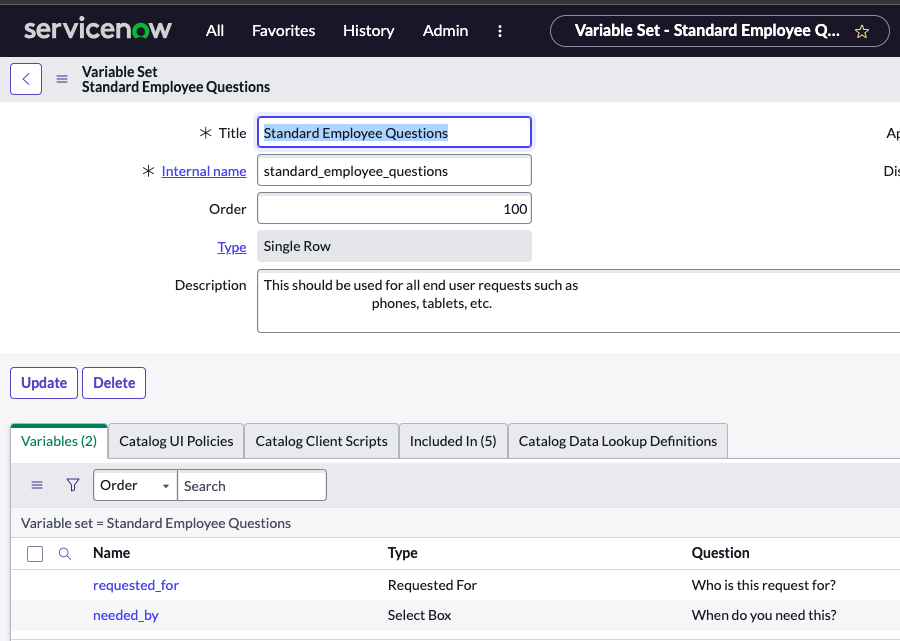
Question: How do you add a variable set to a catalog item?
Answer: Go into maintain items (All > Service Catalog > Catalog Definitions > Maintain Items) and choose a catalog item, in this case Standard Laptop.
Clicking the standard laptop catalog item, scroll down, and you’ll see the variable sets tab at the bottom left. Click edit.
Add standard employee questions from the slushbucket by highlighting it, and then clicking the right arrow. Click save, then click the try it button.
Question: What Variable Types are options to gather information from the requester?
Answer:
1) Multiple Choice
2) Select Box
3) Date
4) Reference
Question: True or False? Catalog UI Policies CANNOT be included within variable sets.
Answer: False. When you translate a catalog item from a form or list, the corresponding variables, variable sets, catalog client scripts and catalog UI polices associated with the catalog item also get translated.
Variables in a Workflow
Question: What are some different types of variables that are available in a Workflow?
Answer:
1) Activity variables. Properties specifically associated with a workflow activity.
2) Workflow input variables. Workflow variables are external values that are passed into and referenced by a workflow during its execution.
3) Workflow scratchpad variables, which allow you to store and share string-based variables as name-value pairs between workflow activities.
Virtual Agent
Question: What is Virtual Agent?
Answer: It is a conversational bot messaging interface, featuring pre-built conversations powered by artificial intelligence. It helps users obtain information, make decisions, and perform common tasks.
Visual Task Boards
Question: What are Visual Task Boards?
Answer: Visual Task Boards (VTB) transform the navigation of lists and forms into an interactive graphical experience. Visual Task Boards provide a visual representation of the work that needs to be done, allowing team members to easily track and prioritize tasks. You can use Visual Task Boards in a variety of contexts, including project management, personal or team task management, and employee onboarding.
With Visual Task Boards, you can view and update multiple task records, which appear as cards that can be moved between lanes. An activity stream on the board displays recent activity so you can easily track changes to tasks. You can add task cards from any table that extends Task to intuitively and easily track updates and edit records directly from the board. Any user can use task boards, regardless of role, though access control rules (ACLs) may limit which cards each user can see. The Visual Task Board interface provides a graphic-rich environment suited for managing and collaborating on records. For example, a support manager might create a board for a team to track their assigned incidents by state in real time.
Question: What are three types of Visual Task Boards?
Answer: Guided boards, flexible boards, and freeform boards.
Guided boards are based on fields values from record lists and records update when cards are moved.
Flexible boards are based on fields values from record lists and records do not update when cards are moved.
Freeform boards are not based on field values from record lists, and records do not update when cards are moved.
Question: How do you see your tasks in the Visual Task Board view? Answer: Right click on any column, and select Visual Task Board. For example, this is what the Visual Task Board looks like for all Incidents when right clicking on the Priority column:
You will now see Incidents by Priority in Visual Task Board view.
Virtual Agent
Question: What is Virtual Agent? Answer: Virtual Agent is a conversational bot platform that provides assistance to help users obtain information, make decisions, and perform common work tasks.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/virtual-agent/concept/virtual-agent-landing-page.html
Question: Virtual Agent provides a personalized customer experience by automating typical Tier 1 support tasks for which of the following?
Answer: 1) Answering FAQs 2) Performing Diagnostics 3) Providing how-to information
W
Widgets
Question: What are Widgets? Answer: Widgets are objects that have been added to dashboards. You can create and manage widgets. Many applications have their own widgets. See an application’s documentation for information about the widgets included with the application.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-now-intelligence/page/use/dashboards/concept/widgets.html
https://docs.servicenow.com/en-US/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/build/service-portal/concept/service-portal-widgets.html
Wildcard Search
Question: What are available list search wildcards? Answer: See the link below for a complete list.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/use/using-lists/task/t_SearchAList.html
Question: What are available list search wildcards? Answer: See the link below for a complete list.
Workflow
Question: What is Workflow? Answer: A workflow comprises the interdependent processes and people required to reach a result that no single participant can achieve alone.
Question: What are the 3 basic components of Workflow? Answer: The three basic components of workflows are: 1. Input – The resources and materials necessary to complete a single step 2. Transformation – The set of parameters that guide how an Input is received and interacted with 3. Output – The resources and materials created that lead in to the next step
https://www.servicenow.com/workflow/learn/digital-workflows-and-automation/what-is-a-workflow/
Workflow Activities
Question: What are the core workflow activities provided in the base system? Answer:
• Approval and rollback workflow activities
• Condition Workflow activities
• Notification workflow activity
• Notify workflow activites
• Subflow activities
• Task workflow activities
• Timer workflow activities
• Utility workflow activities
Question: Which Workflow Activities are included with Orchestration? Answer: The following activities are included with Orchestration:
• Active Directory activity pack
• Orchestration activities
• PowerShell activities
• Puppet activities
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/using-workflows/concept/c_WorkflowActivities.html
Workflow and Flow Designer
- note that Flow Designer has replaced the legacy Workflow Editor.
Question: What is Workflow Editor? Answer: The Workflow Editor is an interface for creating and modifying workflows by arranging and connecting activities to drive processes.
You can manage multiple workflows in the same screen, create custom workflow activities, and use existing activities as data sources. Users with the workflow_creator role can create workflows. Users with the workflow_admin role can create, modify, delete, and publish workflows.
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/workflow/reference/workflow-editor.html
Question: How do you access Workflow Editor? Answer: All > Workflow > Workflow Editor
Question: What is visible on the Workflow Editor Welcome screen? Answer: The New Workflow button.
Question: What are the main components of Flow Designer? Answer:
1) Flows. A flow is an automated process consisting of a trigger and a sequence of actions.
2) Subflows. A subflow is an automated process consisting of a sequence of reusable actions, data inputs, and outputs. In contrast to flows, subflows do not have a trigger but instead run within a flow, another subflow, or a script.
3) Actions. An action is a reusable operation that enables process analysts to automate Now Platform features without having to write code. For example, the Create Record action allows process analysts to generate records in a particular table with particular values when certain conditions occur.
4) Spokes. A spoke is a scoped application containing Flow Designer actions and subflows for managing specific tables. For example, the ITSM Spoke contains actions for managing Incident and Problem records.
5) Actions steps. An action step or step is a single reusable operation within an action. For example, the Create Record step allows action designers to specify the table and field values to use during record creation. Action steps require subject matter expertise with application tables, fields, and business logic.
Question: The applications delivered by ServiceNow are divided into four different workflows. What are they?
Answer:
• IT Workflows
• Employee Workflows
• Customer Workflows
• Creator Workflows
Question: What are common Workflow Activities? Answer: Approvals, Notifications, Conditions, Task, Timers, Utilities
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-application-development/page/administer/flow-designer/concept/flow-designer.html
Question: Must all Workflows have a beginning and an end? Answer: Yes, they absolutely must have a beginning and an end.
Question: What is Workflow Canvas? Answer: After you open or create a new workflow, the system displays the workflow canvas. On the canvas you interact with the Workflow Editor through several different elements: the canvas itself, the canvas tabs, the title bar, the palette, and the palette tabs.
The drawing canvas is where you add activities and configure transitions for checked out workflows. Add an activity by dragging it from the palette to the workflow in the canvas. For more information, see Create a workflow.
Question: What provides the working surface for creating new workflows or editing existing workflows? Answer: The Workflow Canvas?
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/quebec-servicenow-platform/page/administer/workflow/reference/workflow-editor.html
Workflow Stages
Question: Fill in the blanks. The Incident [incident] table has an __ field that indicates progress, but the service catalog uses the field. Answer: Incident State and Stage.
Question: When you edit available activity stages in the Workflow Editor, the list displays which stage values? Answer:
• Waiting for Approval
• Fulfillment
• Delivery
• Request Cancelled
• Completed https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/using-workflows/concept/c_WorkflowStages.html
Workflow Tables
Question: In which table do you find the primary records of workflows? Answer: In the wf_workflow table.
Question: In which table are workflow versions captured? Answer: In the wf_workflow_version
https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-servicenow-platform/page/administer/using-workflows/reference/r_WorkflowTables.html
Workshops
Question: True of False? When documenting requirements, it is important to include the customer’s preferred designed choices. Answer: False.
Workspaces Menu
Question: What does the Workspaces Menu give you access to? Answer: The Workspaces menu provides a list of workspaces you have access to. This item displays only if you have access to a workspace. If you have access to only one workspace, the name of the workspace you have access to displays in the header.
https://docs.servicenow.com/en-US/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/get-started/servicenow-overview/concept/using-the-next-experience-global-header.html
Question: How do you access your Workspace? Answer: Navigate to Workspace Experience > Administration > All Workspaces
There is a tutorial on Workspace here: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/sandiego-platform-user-interface/page/administer/workspace/task/workspace-tutorial-for-agents.html